Публикации
График
Статьи
2026 год
Статьи
-
Formation of the H3CS-Au-SCH3 complex on Au(111): A molecular dynamics study

Thiol-containing compounds represent a key structural motif in the self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on gold. Using molecular dynamics simulations, we investigated the formation of the complex on a Au(111) surface. Our study determines all potential energy barriers for the formation of the complex and reveals the anisotropic nature of diffusion barriers for methylthiolate and gold adatoms on the reconstructed surface. We also discuss the most probable mechanisms underlying the formation of the complex.
Klavsyuk, Andrey L., Syromyatnikov, Alexey G., Yakhin, Ivan Y., Saletsky, Alexander M. Formation of the H3CS-Au-SCH3 complex on Au(111): A molecular dynamics study. Computational Materials Science 263, 114434 (2026) -
Новая кинетическая модель Монте-Карло для исследования магнитных свойств атомных цепочек
Магнитные атомные цепочки имеют потенциальные приложения в различных перспективных областях физики, таких как спинтроника, квантовые коммуникации и квантовые вычисления. Одним из возможных способов исследования магнитных свойств атомных цепочек на больших временных масштабах является кинетический метод Монте-Карло (КММК). В настоящей работе мы предлагаем новую КММК модель, учитывающую зависимость частотных префакторов от параметров цепочки. Наши результаты показывают, что эмпирическое правило Мейера-Нелделя применимо к магнитным системам: более высокие энергетические барьеры соответствуют более высоким частотным префакторам. Используя геодезический метод упругой ленты и гармоническое приближение теории переходного состояния, мы вычислили поправки, обусловленные неколлинеарностью магнитных моментов атомов в переходном состоянии. Обсуждаются ограничения применимости предложенной КММК модели. Показано что, в общем случае, зависимостью частотных префакторов от параметров атомной цепочки нельзя пренебрегать.
Колесников, С. В., Колесникова, И. Н. Новая кинетическая модель Монте-Карло для исследования магнитных свойств атомных цепочек. Вестник Московского университета. Серия 3: Физика, астрономия 81 (1), 2610104 (2026)
2025 год
Статьи
-
Magnetic states of finite-length Mn chains on Pt(332) surface induced by the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction
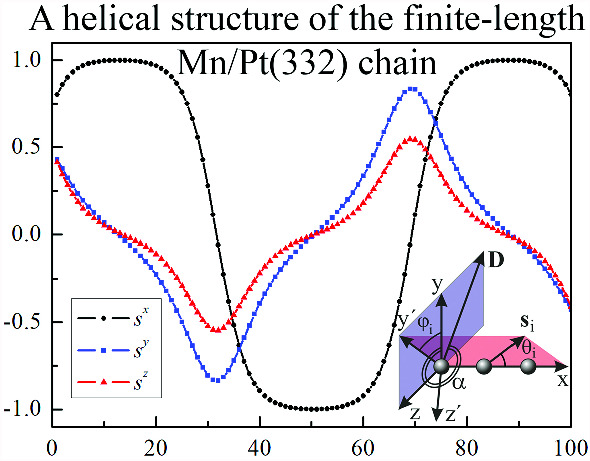
Using the geodesic nudged elastic band method and the harmonic approximation of transition state theory the magnetic properties of finite-length Mn atomic chains on the Pt(332) surface have been investigated. Our study accounted for exchange interaction, magnetic anisotropy energy, Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI), and long-range dipole–dipole interactions. We found that finite-length Mn chains can exhibit both quasicollinear and helical structures, with the DMI at the chain ends playing a crucial role in stabilizing these configurations. The competition between magnetic anisotropy energy and DMI determines the plane in which the helical structures are oriented. Additionally, dipole–dipole interactions contribute to narrowing the domain wall width and reducing the deviation of magnetic moments at the chain ends from the easy magnetization axis. Our results show that the lifetimes of magnetic states are highly sensitive to temperature and chain length. For certain chain lengths, the lifetimes of four or even six different magnetic states are nearly identical or very close. This result may be interesting for future technical applications.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Glazova, E. S., Saletsky, A. M. Magnetic states of finite-length Mn chains on Pt(332) surface induced by the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction. European Physical Journal B 98, 172 (2025) -
Magnetization reversal of finite-length Co and Fe atomic chains on Pt(332) surface: numerical calculations and a new theoretical approach
Different mechanisms of magnetization reversal in finite-length Co and Fe chains on the Pt(332) surface have been investigated, taking into account the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction. It has been found that the magnetization reversal in short atomic chains occurs through the simultaneous reversal of all magnetic moments. In contrast, the magnetization reversal in long atomic chains is facilitated by the formation of domain walls, which exhibit distinct structures for Co and Fe atomic chains. Using the geodesic nudged elastic band method, we have determined the energy barriers for magnetization reversal in chains consisting of 5 to 100 atoms. Additionally, the frequency prefactors have been calculated within the framework of the harmonic approximation of transition state theory. Notably, the dependencies of these prefactors on chain length and external magnetic field are significant and non-monotonic. We propose a theoretical approach that qualitatively describes the numerical dependencies for both the energy barriers and the frequency prefactors. The magnetization curves derived from our theoretical estimates show qualitative agreement with the results of numerical calculations. This analytical approach enables the estimation of the coercive force of atomic chains across a wide range of lengths, temperatures, sweeping rates, and model parameters. The proposed theoretical framework is applicable not only to the Co and Fe chains on the Pt(332) surface but also to a broad class of one-dimensional magnetic systems.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Glazova, E. S., Saletsky, A. M. Magnetization reversal of finite-length Co and Fe atomic chains on Pt(332) surface: numerical calculations and a new theoretical approach. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2025 (5), 053207 (2025) -
Экзотические наноструктуры на поверхности металлов
На сегодняшний день, помимо широко исследуемых нанообъектов, существует целый ряд менее популярных, но от этого не менее интересных экзотических наноструктур, которые по своим физико-химическим свойствам занимают некоторое промежуточное положение. В статье рассмотрены следующие экзотические наноструктуры, формирующиеся в биметаллических системах: атомные сверхрешётки, плоские дендриты, пальцеобразные выступы, связанные наноструктуры, погружённые в первый слой подложки, а также кластеры, формирующиеся под поверхностью на глубине нескольких атомных слоёв. Подробно обсуждаются как экспериментальные методы получения таких наноструктур, так и теоретические подходы к моделированию их формирования. Также обсуждаются физико-химические свойства экзотических наноструктур и возможные перспективы их технического применения.
С. В. Колесников, А. Г. Сыромятников, А. М. Салецкий, А. Л. Клавсюк. Экзотические наноструктуры на поверхности металлов. Успехи физических наук 195 (4), 377-394 (2025)-
Exotic nanostructures on metal surfaces
Today, in addition to widely studied nanoobjects, there are a number of less popular, but no less interesting, exotic nanostructures, which occupy an intermediate position in their physicochemical properties. The article considers the following exotic nanostructures formed in bimetallic systems: atomic superlattices, flat dendrites, finger-shaped protrusions, bound nanostructures embedded in the first layer of a substrate, as well as clusters formed under the surface at a depth of several atomic layers. Both experimental methods for obtaining such nanostructures and theoretical approaches to modeling their formation are discussed in detail. The physicochemical properties of exotic nanostructures and possible prospects for their technical application are also discussed.
Kolesnikov, Sergei V., Syromyatnikov, Aleksei G., Saletsky, Aleksandr M., Klavsyuk, Andrey L. Exotic nanostructures on metal surfaces. Physics-Uspekhi 68 (04), (2024)
-
Тезисы
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Клавсюк, А. Л., Салецкий, А. М. Рост и эволюция нанопроводов Ir на поверхности полупроводника Ge(001). Сборник тезисов IV Международной конференции "Физика конденсированных состояний" ФКС-2025, Стр. 248 (2025).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Клавсюк, А. Л., Салецкий, А. М. Теоретическое исследование формирования нанопроводов Ir на поверхности Ge(001). Сборник тезисов докладов XI Всероссийской научной молодежной школы-конференции "Химия, физика, биология: пути интеграции", 23–25 апреля 2025 года, Стр. 179–180 (2025).
-
Клавсюк, А. Л., Сыромятников, А. Г. Исследование формирования структур при осаждении молекул декантиола на поверхность Au(001). Современная химическая физика XXXVII Симпозиум Сборник тезисов, Стр. 178 (2025).
-
Klavsyuk, A., Syromyatnikov, A., Saletsky, A. Transition-metal impurities on Ge(001): Adsorption, surface diffusion, and magnetic properties studied by density-functional theory. IBCM 2025 (VI International Baltic Conference of Magnetism). 17 – 21 августа 2025. Калининград, Россия. Книга тезисов, Стр. 164 (2025).
-
Глазова, Е. С., Колесников, С. В., Салецкий, А. М. Перемагничивание атомных цепочек Mn на поверхности Pt(332) со спиральной магнитной структурой, обусловленной взаимодействием Дзялошинского-Мория. Сборник тезисов IV Международной конференции "Физика конденсированных состояний" ФКС-2025, (2025).
-
Глазова, Е. С. Перемагничивание атомных цепочек Mn на поверхности Pt(332) в рамках гармонического приближения теории переходного состояния. Материалы Международного молодежного научного форума "Ломоносов-2025", (2025).
2024 год
Статьи
-
Перемагничивание ферромагнитных атомных цепочек кобальта конечной длины
Исследованы различные механизмы перемагничивания ферромагнитных цепочек Co конечной длины на поверхности Pt(664). Установлено, что перемагничивание коротких цепочек происходит за счет одновременного переворота всех магнитных моментов. При большей длине цепочки перемагничивание происходит посредством формирования антидоменной стенки неелевского типа. Перемагничивание длинной цепочки может осуществляться как за счет формирования антидоменной, так и доменной стенки. Геодезическим методом упругой ленты вычислены энергетические барьеры для перемагничивания атомных цепочек длиной от 5 до 100 атомов. В рамках гармонического приближения теории переходного состояния вычислены частотные префакторы. Обнаружена немонотонная и достаточно сильная зависимость частотных префакторов как от длины цепочки, так и от величины внешнего магнитного поля. Построены кривые намагничивания цепочек из атомов Co, найдены значения остаточной намагниченности и коэрцитивной силы цепочек. Проанализированы зависимости коэрцитивной силы от длины цепочки, температуры и скорости изменения магнитного поля.
Колесников С.В., Сапронова Е.С., Салецкий А.М. Перемагничивание ферромагнитных атомных цепочек кобальта конечной длины. Физика металлов и металловедение 125 (7), 779–789 (2024)-
Remagnetization of Finite-Length Ferromagnetic Cobalt Atomic Chains
The remagnetization mechanisms of finite-length ferromagnetic cobalt atomic chains at the Pt(664) surface have been investigated. It has been found that the remagnetization of short chains occurs due to the simultaneous flipping of all magnetic moments. At longer chain lengths, remagnetization occurs through the formation of a N{\'e}el-type anti-clockwise domain wall. The remagnetization of long chains can be achieved through both the formation of anti-clockwise and clockwise domain walls. The energy barriers for remagnetization of atomic chains with lengths ranging from 5 to 100 atoms have been calculated using the geodesic nudged elastic band method. In the framework of the harmonic approximation of the transition state theory, frequency prefactors have been calculated. A non-monotonic and sufficiently strong dependence of the frequency prefactors on both the chain length and an external magnetic field has been identified. The magnetization curves of Co atomic chains have been constructed, and the residual magnetization values and coercive force of the chains have been determined. The dependences of the coercive force on the chain length, temperature, and remagnetization rate of the magnetic field have been analyzed.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Sapronova, E. S., Saletsky, A. M. Remagnetization of Finite-Length Ferromagnetic Cobalt Atomic Chains. Physics of Metals and Metallography 125 (7), 683–692 (2024)
-
-
Моделирование процесса формирования нанопроводов Ir на поверхности Ge(001)
Впервые формирование нанопроводов иридия на поверхности Ge(001) было исследовано с использованием теории функционала плотности и кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Выявлено, что адатомы иридия погружаются в поверхностный слой, в котором и происходит их диффузия. Были выявлены основные диффузионные события, определяющие формирование атомных проводов и их форму. Обнаружена анизотропия диффузии атома иридия в поверхностном слое Ge(001). Выявлено, что отталкивание между атомом иридия и димером иридия приводит к формированию нанопроводов, состоящих из димеров, расположенных через один атомный ряд. Полученные результаты хорошо согласуются с экспериментальными данными.
А. Г. Сыромятников, А. М. Салецкий, А. Л. Клавсюк. Моделирование процесса формирования нанопроводов Ir на поверхности Ge(001). Письма в ЖЭТФ 120, 273–278 (2024)-
Simulation of the Formation of Ir Nanowires on the Ge(001) Surface
The formation of iridium nanowires on the Ge(001) surface has been studied for the first time using the density functional theory and the kinetic Monte Carlo method. It has been found that iridium adatoms are immersed in the surface layer, where they diffuse. The main diffusion events that determine the formation of atomic wires and their shape have been identified. The anisotropy of iridium atom diffusion in the Ge(001) surface layer has been detected. It has been found that the repulsion between the iridium atom and the iridium dimer leads to the formation of nanowires consisting of dimers separated by one atomic row. The results obtained are in good agreement with experimental data.
Syromyatnikov, A. G., Saletsky, A. M., Klavsyuk, A. L. Simulation of the Formation of Ir Nanowires on the Ge(001) Surface. JETP Letters 120 (4), 265–269 (2024)
-
-
Энергетические барьеры для перемагничивания атомных цепочек из Co на поверхности Pt(664) с учетом взаимодействия Дзялошинского-Мория
В рамках непрерывной XY-модели получены аналитические выражения, позволяющие вычислять время спонтанного перемагничивания атомных цепочек конечной длины. На примере системы Co/Pt(664) показано, что предложенный метод дает хорошее согласие с результатами численного моделирования в пределе коротких и длинных атомных цепочек. А для атомных цепочек промежуточной длины его можно использовать для получения ограничения сверху на время спонтанного перемагничивания. Предложенный метод имеет широкую область применения как по температуре, так и по значениям физических параметров, характеризующих магнитные свойства атомных цепочек. Таким образом, он может быть использован не только для системы Co/Pt(664), но и для других похожих систем.
С. В. Колесников, Е. С. Сапронова. Энергетические барьеры для перемагничивания атомных цепочек из Co на поверхности Pt(664) с учетом взаимодействия Дзялошинского-Мория. Поверхность. Рентгеновские, синхротронные и нейтронные исследования 2, 36–43 (2024)-
Energy Barriers for the Spontaneous Magnetization Reversal of Atomic Co Chains on the Surface Pt(664) in the Model of Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya Interaction
Within the framework of the continuous XY model, analytical expressions are derived to calculate the time of the spontaneous magnetization reversal of finite-length atomic chains on the surface of a metal. The interaction of magnetic moments of atoms is described by the classical Hamiltonian, which includes the Heisenberg exchange interaction, the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction, and the magnetic-anisotropy energy. Using the example of the Co/Pt(664) system, it is demonstrated that the proposed method exhibits good agreement with the results of numerical simulations for both short and long atomic chains. For atomic chains of intermediate length, it can be utilized to obtain an upper bound on the time of spontaneous magnetization reversal. We obtained dependences of the time of spontaneous magnetization reversal for finite-length Co atomic chains, taking into account the exchange integral, parameters characterizing the magnetic anisotropy, and the projection of the Dzyaloshinskii vector onto the axis perpendicular to the plane containing the magnetic moments of atoms. The proposed method is applicable over a wide range of temperatures and values of physical parameters that characterize the magnetic properties of atomic chains. Thus, it can be employed not only for the Co/Pt(664) system but also for other similar systems.
Kolesnikov S.V., Sapronova E.S. Energy Barriers for the Spontaneous Magnetization Reversal of Atomic Co Chains on the Surface Pt(664) in the Model of Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya Interaction. Journal of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques 18, 150–155 (2024)
-
-
Зависимость параметров роста атомных цепочек от характера изменения температуры подложки
Данная работа посвящена исследованию роста и эволюции одномерных наноструктур на металлических ступенчатых поверхностях при помощи кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Было показано, что при нагреве подложки и при ее охлаждении распределение длин таких наноцепочек изменяется по-разному. Помимо этого были описаны закономерности, связывающие характер изменения распределения длин и относительные величины диффузионных барьеров для адатомов на поверхности, что позволит предсказать свойства распределения длин образующихся одномерных наноструктур.
А. Г. Сыромятников, С. А. Кудряшов, А. Л. Клавсюк, А. М. Салецкий. Зависимость параметров роста атомных цепочек от характера изменения температуры подложки. Поверхность. Рентгеновские, синхротронные и нейтронные исследования 2, 44–47 (2024)-
Dependence of Growth Parameters of Atomic Chains on Changes in the Substrate Temperature
The growth and evolution of one-dimensional nanostructures on metal stepped surfaces were studied using the kinetic Monte Carlo method. The distribution of nanochain lengths was shown to change differently when the substrate was heated and cooled. Regularities are described that connect the nature of changes in the length distribution and the relative values of diffusion barriers for adatoms on the surface, which will make it possible to predict the length distribution of the resulting one-dimensional nanostructures.
Syromyatnikov, A.G., Kudryashov, S.A., Klavsyuk, A.L., Saletsky, A.M. Dependence of Growth Parameters of Atomic Chains on Changes in the Substrate Temperature. Journal of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques 18, 156–159 (2024)
-
-
Моделирование диффузии атома меди на графене методом молекулярной динамики
Приведены результаты исследования влияния геометрических и термодинамических параметров термического испарения и осаждения меди на графен, лежащий на поверхности Cu(111), на адсорбцию атомов меди, а также их поверхностную диффузию. Моделирование проводилось методом классической молекулярной динамики с использованием цепочек термостатов Нозе–Гувера. Межатомные взаимодействия определяли с использованием потенциалов Терсоффа–Бреннера, Росато–Жиллопа–Легранда и модифицированного потенциала Морзе. Сформулирован и протестирован простой критерий термализации адатомов на графене, лежащем на поверхности Cu(111). Исследованы средняя длина и среднее время свободного пробега атома меди до и после термализации при низкой (7 К) и комнатной температурах графена для двух температур испарения. Найдена вероятность адсорбции атома меди. Построены распределения по направлениям движения адатомов при равновесной диффузии. Показано, что распределения длины и времени свободного пробега имеют экспоненциальный вид. Исследовано влияние подложки Cu(111) на диффузию атома Cu на графене. Полученные результаты могут быть использованы для моделирования роста нанокластеров меди на графене кинетическим методом Монте-Карло.
С. В. Худяков, С. В. Колесников, А. М. Салецкий. Моделирование диффузии атома меди на графене методом молекулярной динамики. Поверхность. Рентгеновские, синхротронные и нейтронные исследования 2, 48–53 (2024)-
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Diffusion of a Copper Atom on Graphene
The results of studying the effect of geometric and thermodynamic parameters of thermal evaporation and copper deposition on graphene lying on the Cu(111) surface on the adsorption of copper atoms, as well as their surface diffusion, are presented. The simulation is carried out by classical molecular dynamics using chains of Nose–Hoover thermostats. Interatomic interactions are determined by the Tersoff–Brenner, Rosato–Guillope–Legrand, and modified Morse potentials. A simple criterion for the thermalization of adatoms on graphene lying on a Cu(111) surface is formulated and tested. The average length and the mean free path time of the copper atom before and after thermalization at low (7 K) and room temperatures are studied for two evaporation temperatures. The probability of adsorption of the copper atom is found. The distributions along the directions of motion of adatoms during equilibrium diffusion are constructed. The distributions of the free path length and time are shown to have an exponential form. The influence of the Cu(111) substrate on the diffusion of the Cu atom on graphene is studied. The results obtained can be used to simulate the growth of copper nanoclusters on graphene by the kinetic Monte Carlo method.
Khudyakov, S.V., Kolesnikov, S.V., Saletsky, A.M. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Diffusion of a Copper Atom on Graphene. Journal of Surface Investigation: X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques 18, 160–165 (2024)
-
Тезисы
-
Сапронова, Е. С. Перемагничивание атомных цепочек Co на поверхности Pt(664) с учётом зависимости частотных префакторов от длины цепочки. Материалы Международного молодежного научного форума "Ломоносов-2024", (2024).
2023 год
Статьи
-
Ground and excited states of the finite-size Fe chains on Pt(664) surface
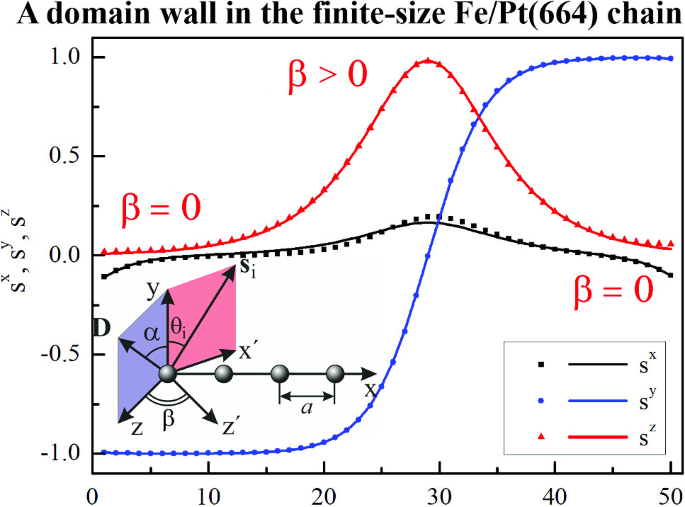
The energy barriers for magnetization reversal of the finite-size Fe chains on Pt(664) surface have been calculated using the geodesic nudged elastic band method. The Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction and the dipole–dipole interaction have been taken into account. It has been found that the ground states of Fe/Pt(664) atomic chains are non-collinear at the ends. The magnetization reversal of short atomic chains occurs without the formation of the domain walls. While the magnetization reversal of the long atomic chains occurs via the formation of the domain walls. The interplay between the magnetic anisotropy energy and the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction leads to the rotation of the domain wall plane. As a result, the domain walls in Fe/Pt(664) atomic chains are intermediate configurations between Bloch and Néel walls. The dipole–dipole interaction weakly influences the value of the energy barriers and may be neglected. It is shown that the presented results can be explained in the framework of the classical continuous model. The constructed approximate functions correctly describe all features of the ground states and the saddle points. The structure of the domain walls and the dependencies of the energy barriers on the parameters of the model are different from the case of the Co/Pt(664) system investigated recently.
Kolesnikov, Sergey V., Sapronova, Ekaterina S., Kolesnikova, Inna N. Ground and excited states of the finite-size Fe chains on Pt(664) surface. The European Physical Journal B 96 (12), 163/1–163/10 (2023) -
An influence of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction on the magnetization reversal process of the finite-size Co chains on Pt(664) surface

Energy barriers for magnetization reversal of the finite-size Co chains on Pt(664) surface are calculated with taking the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction into account. For the numerical calculations the geodesic nudged elastic band method is employed. It has been found that the ground states of such atomic chains are noncollinear. The magnetization reversal of short atomic chains occurs without the formation of domain walls. At the same time, there are two nonequivalent ways for the magnetization reversal of longer atomic chains. The first way is the formation of clockwise domain wall (CDW) and the second way is the formation of anticlockwise domain wall (ACDW). The second way is energetically preferable. It is shown that a metastable state corresponding to the location of ACDW in the middle of the atomic chain can appear. The variation of the parameters of the Hamiltonian shows that the magnetization reversal via the CDW formation can occur only in a certain region of the parameters. The influence of the long-range dipole–dipole interaction on the energy barriers for the magnetization reversal is also investigated. It is shown that the most of the presented results can be satisfactory explained in the framework of the XY-model. The magnetic configurations of the atomic chain near the local minima and the saddle points can be approximated with simple analytical functions.
S.V. Kolesnikov, E.S. Sapronova, I.N. Kolesnikova. An influence of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction on the magnetization reversal process of the finite-size Co chains on Pt(664) surface. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 579, 170869 (2023)
Тезисы
- Klavsyuk, A. L., Kolesnikov, S. V., Sapronova, E. S. The magnetization reversal of the finite-size Co and Fe chains on Pt(664) surface: a comparation of the analytical and the computational results. V International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2023 (IBCM-2023) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 188 (2023).
- Kolesnikov, S. V., Sapronova, E. S. An influence of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction on the magnetization reversal of the finite-size Co and Fe chains. V International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2023 (IBCM-2023) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 35 (2023).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Кудряшов, С. А., Салецкий, А. М., Клавсюк, А. Л. Градиент температуры как способ управления ростом одномерных наноструктур на ступенчатых поверхностях. Тезисы III Международной конференции "Физика конденсированных состояний" ФКС-2023, посвященной 60-летию ИФТТ РАН, Стр. 170 (2023).
-
Кудряшов, С. А. Исследование формирования квантовых точек олова в матрице германия. XXX Международная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых по фундаментальным наукам "Ломоносов—2023". Секция "Физика", Стр. 881 (2023).
-
Сапронова Е. С. Влияние взаимодействия Дзялошинского-Мория на время перемагничивания атомных цепочек Co на поверхности Pt(664). XXX Международная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых по фундаментальным наукам "Ломоносов—2023". Секция "Физика", Стр. 798–799 (2023).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Кудряшов, С. А., Салецкий, А. М., Клавсюк, А. Л. Энергетические барьеры для перемагничивания атомных цепочек из Co на поверхности Pt(664) с учетом взаимодействия Дзялошинского-Мория. Тезисы III Международной конференции "Физика конденсированных состояний" ФКС-2023, посвященной 60-летию ИФТТ РАН, Стр. 166 (2023).
-
Худяков С. В., Колесников С. В. Моделирование диффузии атома меди на графене методом молекулярной динамики. Тезисы III Международной конференции "Физика конденсированных состояний" ФКС-2023, посвященной 60-летию ИФТТ РАН, Стр. 125 (2023).
2022 год
Статьи
-
Self-Assembled Decanethiolate Monolayers on Au(001): Expanding the Family of Known Phases

We have studied decanethiolate self-assembled monolayers on the Au(001) surface. Planar and striped phases, as well as disordered regions, have formed after exposing the Au surface to a decanethiol solution. The planar phases that we observe have a hexagonal symmetry and have not been previously reported for thiols on the Au(001) surface and have lower coverage compared to that of the other known thiol planar phases such as the square α phase. The striped phases that we observe are similar to the previously reported β phase but still feature unit cells that cannot be modeled as the archetype, and the coverage is also somewhat lower. The disordered decanethiolate regions are more dynamic compared to the ordered phases, confirmed with I(t) spectroscopy. This suggests that in these regions the coverage is too low in order to form ordered decanethiolate phases. Our findings contribute to the growing family of possible decanethiol formations on the Au(001) surface, for which still less is known compared to the extensive overview present for the Au(111) surface.
Tsvetanova, Martina, Syromyatnikov, Alexey G., van der Meer, Thomas, van Houselt, Arie, Zandvliet, Harold J. W., Klavsyuk, Andrey L., Sotthewes, Kai. Self-Assembled Decanethiolate Monolayers on Au(001): Expanding the Family of Known Phases. Langmuir 38 (33), 10202–10215 (2022) -
Influence of Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya and Dipole–Dipole Interactions on Spontaneous Magnetization Reversal Time of Finite-Length Co Chains on Pt(664) Surfaces
The spontaneous magnetization reversal of the finite-length Co chains on Pt(664) surface is investigated in the framework of the classical effective theory. The effective theory includes the Heisenberg exchange interaction, magnetic anisotropy energy, Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI), and dipole–dipole interaction. The geodesic-nudged elastic band method is employed for calculations of the energy barriers for magnetization reversal of the finite-length Co chains. The calculation of the spontaneous magnetization reversal time shows that the dipole–dipole interaction can be neglected at a temperatures higher than 10.9 K. DMI can be neglected at temperatures higher than 60.2 K. This means that DMI can significantly influence the magnetization reversal process at low temperatures and should be taken into account.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Sapronova, E. S. Influence of Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya and Dipole–Dipole Interactions on Spontaneous Magnetization Reversal Time of Finite-Length Co Chains on Pt(664) Surfaces. IEEE Magnetics Letters 13, Art. No. 2505905 (1–5) (2022) -
Distribution of atomic chain lengths: Effect of local temperature profile

A challenging aim of current research in one-dimensional physics is the search for optimal conditions for the formation of well-ordered chains. The effect of local temperature profile was investigated using large-scale kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. It was found that well-ordered long chains are formed in the presence of a temperature gradient in the sample near the critical temperature. Furthermore, it was shown how the size distribution of chains changes during annealing and cooling. The observed change mechanism of the chain length during the annealing or cooling will be useful in industry for creating atomic chains with a given length.
Alexey G. Syromyatnikov, Sergey A. Kudryashov, Alexander M. Saletsky, Andrey L. Klavsyuk. Distribution of atomic chain lengths: Effect of local temperature profile. Chemical Physics Letters 802, 139796 (2022) -
Low coverage disordered decanethiol monolayers on Au(001): A conjecture regarding the formation of Au-adatom-molecule complexes

We present a scanning tunneling microscopy study of decanethiol on Au(001) in the low coverage regime. As expected, the hex reconstruction is lifted, however, no ordered decanethiol phases form. We observe large areas free of Au islands and covered with a disordered decanethiol phase. I(t) spectroscopy measurements suggest that this disordered phase is dynamic and most likely comprises diffusing Au adatoms, decanethiol molecules, and/or Au-adatom-decanethiol molecule complexes. We have performed density functional theory calculations and show that the activation barrier for diffusion is lower when Au-adatom-molecule complexes are considered in comparison to the case of bare molecule. These findings suggest that although no vacancy pits form on Au(001), Au-adatoms expelled during the lifting of the hex reconstruction may be still important for the diffusion of thiol molecules on this surface.
Martina Tsvetanova, Alexey G. Syromyatnikov, Harold J.W. Zandvliet, Andrey L. Klavsyuk, Kai Sotthewes. Low coverage disordered decanethiol monolayers on Au(001): A conjecture regarding the formation of Au-adatom-molecule complexes. Applied Surface Science 594, 153364 (2022) -
Формирование дендритов Pt/Cu на ступенях поверхности Cu(111)
Формирование кластеров Pt/Cu на ступенчатой поверхности Cu(111) исследовано теоретически с помощью самообучающегося кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Показано, что, варьируя условия роста кластеров Pt/Cu, можно добиться формирования различных наноструктур: вытянутых и разветвленных дендритов, а также пальцеобразных выступов различной формы. Установлено, что форма кластеров определяется в основном тремя параметрами: температурой системы, относительной концентрацией платины и типом ступени, на которой происходит рост кластера. Для роста дендритов необходимо выполнение двух условий: температура системы должна быть около 200 K или ниже, и в системе должны присутствовать атомы Pt. При этом, в зависимости от типа ступени растут либо дендриты, вытянутые в направлении перпендикулярно ступени, либо сильно разветвленные дендриты. При комнатной температуре на ступенях растут пальцеобразные выступы, причем их длина также зависит от типа ступени. Различие формы кластеров на различных ступенях является следствием анизотропии диффузии атомов вблизи углов кластеров и может быть объяснено исходя из анализа энергетических барьеров для прыжков атомов по поверхности Cu(111).
Докукин, С. А., Колесников, С. В., Салецкий, А. М. Формирование дендритов Pt/Cu на ступенях поверхности Cu(111). Журнал экспериментальной и теоретической физики 162 (5), 686–692 (2022)-
Growth of the Pt/Cu Dendrites on Stepped Cu(111) Surface
The formation of Pt/Cu clusters on a stepped Cu(111) surface has been theoretically investigated using the self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo method. It has been shown that by varying Pt/Cu cluster growth conditions, one can prepare different nanostructures, such as spatially extended and branching dendrites and fingers of different geometry. It has been found that the shape of clusters depends mainly on three parameters: temperature, platinum relative concentration, and the type of step on which the cluster grows. Dendrites grow under the following conditions: the temperature in the system must be no higher than 200 K, and the system must contain platinum atoms. Depending on the type of step, either dendrites extended normally to the step or branching dendrites arise. At room temperature, fingers grow on steps, the length of fingers also being dependent on the type of step. Different shapes of clusters on different steps arise from the anisotropic diffusion of atoms near the corners of clusters, which can be explained by taking into account energy barriers for atom hops over the Cu(111) surface.
Dokukin, S. A., Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M. Growth of the Pt/Cu Dendrites on Stepped Cu(111) Surface. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 135 (5), 671–675 (2022)
-
-
Влияние диполь-дипольного взаимодействия на время перемагничивания атомных цепочек конечной длины
Перемагничивание атомных цепочек на поверхности металлов исследовано теоретически с помощью разработанного ранее аналитического метода и геодезического метода упругой ленты. Атомные цепочки могут быть разделены на три группы: цепочки с малой, средней и большой шириной доменной стенки. Показано, что диполь-дипольное взаимодействие приводит к увеличению среднего времени спонтанного перемагничивания цепочек ФМ∥ и АФМ⊥ и уменьшению времени перемагничивания цепочек ФМ⊥ и АФМ∥. Для цепочек ФМ⊥ и АФМ⊥ с доменной стенкой средней ширины учет диполь-дипольного взаимодействия приводит к появлению энергетического барьера между двумя состояниями доменной стенки, отличающимися направлением вращения магнитных моментов. Перемагничивание атомных цепочек из третьей группы может происходить двумя способами: либо все магнитные моменты переворачиваются одновременно, либо по очереди. Переход от одного режима перемагничивания к другому происходит при критической длине N0. При этом влияние диполь-дипольного взаимодействия наиболее существенно при длине цепочки, близкой к N0. Численные оценки показали, что в некоторых случаях учет диполь-дипольного взаимодействия может изменить время перемагничивания цепочки на порядок величины.
Колесников, С. В., Сапронова, Е. С. Влияние диполь-дипольного взаимодействия на время перемагничивания атомных цепочек конечной длины. Журнал экспериментальной и теоретической физики 162 (5), 708–717 (2022)-
Effect of a Dipole-Dipole Interaction on the Time of Magnetization Reversal of Finite-Length Atomic Chains
The magnetization reversal of atomic chains on metal surfaces has been theoretically studied using the analytical method developed earlier and the geodesic nudged elastic band method. The atomic chains can be divided into the following three types: chains with a small, intermediate, and large domain wall width. A dipole–dipole interaction is shown to cause an increase in the average spontaneous magnetization reversal time of FM|| and AFM⊥ chains and a decrease in the magnetization reversal time of FM⊥ and AFM|| chains. For FM⊥ and AFM⊥ chains with a medium-width domain wall, taking into account a dipole–dipole interaction leads to the appearance of an energy barrier between two states of a domain wall differing in the direction of rotation of magnetic moments. The magnetization reversal of atomic chains from the third type can occur in the following two ways: all magnetic moments are reversed either simultaneously or one by one. The transition from one magnetization reversal mode to another occurs at a critical length N0. The effect of a dipole–dipole interaction is most significant when the chain length is close to N0. Numerical estimations have shown that taking into account a dipole–dipole interaction can change the magnetization reversal time of a chain by an order of magnitude in some cases.
S. V. Kolesnikov, E. S. Sapronova. Effect of a Dipole-Dipole Interaction on the Time of Magnetization Reversal of Finite-Length Atomic Chains. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 135 (5), 690–697 (2022)
-
-
Two growth modes of nanostructures near Cu(111) step edges in CoCu and PtCu surface alloys
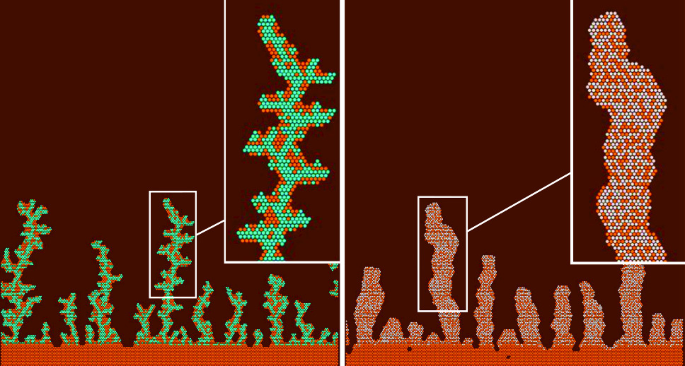
The formation of CoCu and PtCu alloys on the stepped Cu(111) substrate was simulated. Dendritic and finger-like protrusions grow near the edges of the steps. The shape and the internal structure of the protrusions depend on the type of the step edge, temperature and concentrations of impurity atoms. The internal structure and the shape of the protrusions are significantly different in PtCu and CoCu alloys. Pt atoms tend to be surrounded by Cu atoms and Co atoms tend to combine into Co backbones. The dendritic protrusions usually grow at 200 K and the finger-like protrusions usually grow at 300 K. The shape of the protrusions also depends on the type of the step edge and the concentration of impurity atoms. The main differences of PtCu and CoCu protrusions can be explained by the values of the diffusion barriers of the key processes.
S. A. Dokukin, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Two growth modes of nanostructures near Cu(111) step edges in CoCu and PtCu surface alloys. The European Physical Journal B 95 (9), Art. No. 161 (2022) -
Two possible ways of forming ordered magnetic chains on a metal surface: Monte Carlo simulations
Evolution of Co chains on Cu(997) surface and mixed CoNi chains on Ir(001) surface is investigated on the atomic scale by performing Monte Carlo simulations. It was found that ordered chains can be formed from a single metal with a temperature gradient or from an alloy of metals. It is shown how the chain lengths change during annealing and cooling. The results of our simulations will be useful for creating a new generation of magnetic materials.
Alexey Syromyatnikov, Andrey Klavsyuk, Alexander Saletsky. Two possible ways of forming ordered magnetic chains on a metal surface: Monte Carlo simulations. IEEE Magnetics Letters 13, Art. No. 6101403 (1–4) (2022) -
An estimation of magnetic properties of existing and prospective atomic chains in the framework of the Heisenberg Model
In the present investigation we use the analytical method for estimation of magnetic properties of a wide range of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic single-atomic and biatomic chains. It is found that the biatomic chains can be used as a bit of information at higher temperatures than the same single-atomic chains. At the same time, the ratio between the spontaneous and induced remagnetization times is lower in the case of biatomic chains. According to our analysis the Co chains on Rh(553) surface seems the most prospective to the creation of stable bits of information. The effects of nitriding the substrate or oxidation the atomic chain is discussed. The analysis of magnetodynamic properties of ferromagnetic chains showed that the usage of atomic chains gives an opportunity to construct the magnetic materials with wide range of physical properties.
Sergey Kolesnikov, Ekaterina Sapronova. An estimation of magnetic properties of existing and prospective atomic chains in the framework of the Heisenberg Model. IEEE Magnetics Letters 13, Art. No. 2501205 (1–5) (2022) -
Improved kinetic Monte Carlo models for computational and analytical investigations of the magnetic properties of finite-size atomic chains
Two improved kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) models for investigations of the magnetic properties of finite-size atomic chains are presented. These models take into account the possible noncollinearity of magnetic moments. The spontaneous remagnetization of ferromagnetic Co chains on the Pt(997) surface and antiferromagnetic Fe chains on the Cu<sub>2</sub>N/Cu(001) surface is investigated in the framework of our models. The results are compared with the results of the simple kMC model. It is also shown that a single domain-wall approximation can be successfully used to estimate the reversal time of the magnetization. Therefore, the improved kMC models can be used for analytical calculations as well as for computer simulations.
S. V. Kolesnikov, I. N. Kolesnikova. Improved kinetic Monte Carlo models for computational and analytical investigations of the magnetic properties of finite-size atomic chains. Europhysics Letters 137 (5), 56003 (2022) -
Dendritic Growth of Co/Cu Nanostructures on Stepped Cu(111) Surface
The self-learning kinetic Monte-Carlo simulations are applied to simulate the growth of CoCu protrusions near step edges on Cu(111) substrate at various temperatures, deposition fluxes and relative concentrations. The shape of the dendritic protrusions depends on the relative concentration of Co atom. The dependence of the fractal dimension of Co-Cu protrusions on the relative concentration of Co atoms can be monotonic or non-monotonic depending on temperature. The protrusions have Co backbones which fractal dimension differs from the fractal dimension of the entire Co-Cu protrusion.
Sergei Dokukin, Sergey Kolesnikov, Alexander Saletsky. Dendritic Growth of Co/Cu Nanostructures on Stepped Cu(111) Surface. IEEE Magnetics Letters 13, Art. No. 6101705 (1–4) (2022)
Тезисы
-
Кудряшов, С. А. Формирование одномерных атомных структур серебра на поверхности платины. XXIX Международная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых по фундаментальным наукам «Ломоносов—2022». Секция «Физика». Сборник тезисов, Стр. 572–573 (2022).
-
Сапронова, Е. С. Оценка времени перемагничивания атомных цепочек с учётом влияния диполь-дипольного взаимодействия. XXIX Международная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых по фундаментальным наукам «Ломоносов—2022». Секция «Физика». Сборник тезисов, Стр. 495–496 (2022).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Кудряшов, С. А., Клавсюк, А. Л., Салецкий, А. М. Создание упорядоченных атомных цепочек с помощью градиента температуры. Сборник тезисов докладов IX Всероссийской научной молодежной школы-конференции "Химия, физика, биология: пути интеграции", Стр. 166–167 (2022).
2021 год
Статьи
-
Формирование и свойства металлических атомных цепочек и проводов
Рассматривается актуальное состояние многообещающей области современной физики --- изучения физических свойств металлических нанопроводов и атомных цепочек. Привлекательность одномерных наноструктур обусловлена как перспективностью их практического применения, так и возможностью проверки с их помощью различных теоретических моделей и подходов посредством сравнения теоретических результатов с экспериментальными данными. Описаны экспериментальные условия, при которых металлические нанопровода формируются на поверхностях металлов и полупроводников. Особое внимание уделено теоретическим моделям, описывающим сценарий роста нанопроводов на различных поверхностях. Дан анализ основных экспериментально определяемых факторов, влияющих на распределение длин нанопроводов. Показано, что распределение длин нанопроводов на поверхности металлов и полупроводников зависит не только от внешних параметров, но и от времени их формирования. Рассмотрены магнитные свойства атомных цепочек конечной длины, расположенных на поверхностях металлических и полупроводниковых кристаллов. Показана корреляция между структурными, электронными и магнитными свойствами нанопроводов. Установлено влияние нанопроводов на электронные свойства поверхностей, на которых они формируются. Объяснена природа краевых состояний. Показано влияние длины нанопровода на электронные состояния его атомов. Обсуждается эффект Рашбы для металлических нанопроводов на поверхности полупроводников, представлен анализ влияния величины обменной энергии между атомами и энергии магнитной анизотропии на макроскопические характеристики нанопроводов, такие как критическая температура и время спонтанного перемагничивания.
А. Г. Сыромятников, С. В. Колесников, А. М. Салецкий, А. Л. Клавсюк. Формирование и свойства металлических атомных цепочек и проводов. Успехи физических наук 191 (7), 705–737 (2021)-
Formation and properties of metallic atomic chains and wires
We discuss the current state of a promising area of modern physics, the study of the physical properties of metal nanowires and atomic chains. One-dimensional nanostructures are attractive because of both the promise of their practical applications and the possibility of using them to test various theoretical models and approaches by comparing theoretical results with experimental data. We describe experimental conditions under which metal nanowires form on metal and semiconductor surfaces. We give special attention to theoretical models describing the scenario of nanowire growth on various surfaces. We analyze the main experimentally determined factors that affect the distribution of nanowire lengths. We show that the distribution of nanowire lengths on metal and semiconductor surfaces depends not only on external parameters but also on the formation time. We consider the magnetic properties of finite-length atomic chains located on the surfaces of metal and semiconductor crystals. We demonstrate a correlation among the structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of nanowires. We elucidate the effect that nanowires exert on the electronic properties of the surface on which they form. The nature of edge states is explained. The electron states of nanowire atoms are shown to be sensitive to the nanowire length. We discuss the Rashba effect for metal nanowires on a semiconductor surface and analyze how the exchange energy between atoms and the magnetic anisotropy energy affect the macroscopic characteristics of nanowires, such as their critical temperature and the time of spontaneous magnetization reversal.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Formation and properties of metallic atomic chains and wires. Physics-Uspekhi 64 (7), 671–701 (2021)
-
-
Formation of Cu-Pt nanocontacts in STM breaking junction simulations: MD simulations and one-dimensional diffusion model
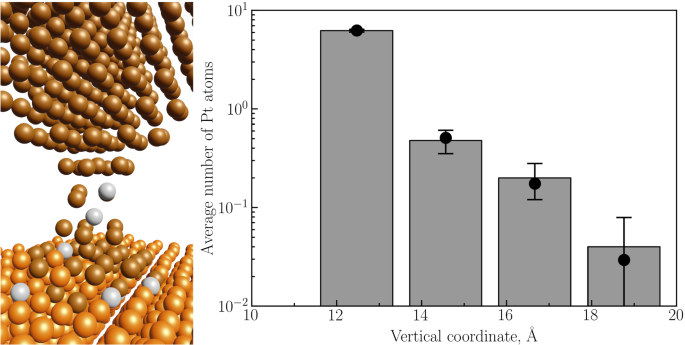
In this paper, we propose a new theoretical approach that combines classical MD method and a one-dimensional diffusion model. We have shown that our approach allows to extrapolate the results of MD simulations to the experimental timescale. As an example, the formation of Cu–Pt nanocontacts in the STM-BJ experiments was investigated. STM-BJ simulations with copper STM tips and Cu–Pt surface alloys were performed in a wide range of temperatures (300–900 K), number of Pt atoms in the substrate (1–7) and for different orientations ((100), (110) and (111)) of the STM tip. Using our approach, we predicted that it is possible to use the STM-BJ technique to prepare Cu–Pt nanocontacts. The presented approach should work well in all cases when the diffusion of atoms occurs via interlayer jumps.
S. A. Dokukin, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Formation of Cu-Pt nanocontacts in STM breaking junction simulations: MD simulations and one-dimensional diffusion model. The European Physical Journal B 94 (4), 85 (1–8) (2021) -
Влияние процесса нагрева и охлаждения на длины одномерных атомных структур
Впервые кинетическим методом Монте-Карло исследовано влияние нагрева и охлаждения на длины одномерных атомных структур. Показано, что переход из одного равновесного состояния в другое при нагреве и охлаждении происходит по-разному. Выявлено, что выше некоторой критической температуры система за время проведения эксперимента быстро достигает термодинамического равновесия, а ниже критической температуры диффузия атомов замедляется и система остается в неравновесном состоянии, которое и наблюдается в большинстве экспериментов.
Сыромятников, А. Г., Кудряшов, С. А., Салецкий, А. М., Клавсюк, А. Л. Влияние процесса нагрева и охлаждения на длины одномерных атомных структур. Журнал экспериментальной и теоретической физики 160 (3), 410–414 (2021)-
Effect of Heating and Cooling on the Lengths of 1D Atomic Structures
The effect of heating and cooling on the lengths of 1D atomic structures was investigated for the first time by the Monte Carlo method. It is shown that transitions from one equilibrium state to another during heating and cooling are different. It is found that above a certain critical temperature, the experimental system rapidly reaches thermodynamic equilibrium, while below the critical temperature, atomic diffusion is slowed down, and the system remains in a nonequilibrium state, which is observed in most experiments.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, S. A. Kudryashov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Effect of Heating and Cooling on the Lengths of 1D Atomic Structures. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 133 (3), 347–350 (2021)
-
-
Formation of embedded Co nanostructures in Cu(001) surface under electromigration
Formation of embedded Co nanostructures in Cu(001) surface under electromigration is investigated on the atomic scale by performing self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) simulations. The analysis of simulation results reveals the following important result. The electromigration of vacancies does not influence on the self-organization of Co nanostructures in the first layer of Cu(001) surface at all values of current density, which can be achieved in experiments.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Klavsyuk, A. L., Saletsky, A. M. Formation of embedded Co nanostructures in Cu(001) surface under electromigration. Modern Physics Letters B 35 (5), 2150090 (2021) -
Исследование процессов формирования наноконтактов Pt–Cu при погружении иглы сканирующего туннельного микроскопа в поверхностный сплав Pt–Cu методом компьютерного моделирования
Методом молекулярной динамики исследовано формирование наноконтактов при погружении иглы сканирующего туннельного микроскопа (СТМ) в поверхностный сплав Pt/Cu. Установлено, что атомы Pt движутся в наноконтакте меди посредством прыжков по атомным слоям в направлении от поверхности меди к основанию СТМ-иглы, в то время как атомы Cu движутся в противоположном направлении. Исследовано формирование наноконтактов при различной ориентации СТМ-иглы, температуре от 300 Kдо 800 K и разном количестве атомов Pt непосредственно под СТМ-иглой. Показано, что вероятность формирования смешанного Pt–Cu наноконтакта может достигать 50%.
Докукин, С. А., Колесников, С. В., Салецкий, А. М. Исследование процессов формирования наноконтактов Pt–Cu при погружении иглы сканирующего туннельного микроскопа в поверхностный сплав Pt–Cu методом компьютерного моделирования. Журнал экспериментальной и теоретической физики 160 (3), 426–433 (2021)-
Study of Pt–Cu Nanocontact Formation Processes during the Indentation of a Scanning Tunneling Microscope Tip into a Pt/Cu Surface Alloy by Computer Simulations
The formation of nanocontacts during the indentation of a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) tip into a Pt/Cu surface alloy has been studied by the molecular dynamics method. It has been established that the Pt atoms move in the copper nanocontact through jumps over atomic layers in the direction from the copper surface to the base of the STM tip, while the Cu atoms move in the opposite direction. The formation of nanocontacts for various orientations of the STM tip, a temperature from 300 to 800 K, and various numbers of Pt atoms immediately beneath the STM tip has been studied. It is shown that the probability of the formation of a mixed Pt–Cu nanocontact can reach 50%.
S. A. Dokukin, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Study of Pt–Cu Nanocontact Formation Processes during the Indentation of a Scanning Tunneling Microscope Tip into a Pt/Cu Surface Alloy by Computer Simulations. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 133 (3), 360–365 (2021)
-
Тезисы
- Сыромятников А. Г., Клавсюк А. Л., Салецкий А. М. Процессы формирования и структурные свойства металлических атомных проводов. Материалы Конференции Ломоносовские чтения 2021, секция "Физика", 1, (2021).
- Докукин С.А., Колесников С.В., Салецкий А.М. Моделирование методом молекулярной динамики формирования Cu-Pt наноконтактов. Материалы Конференции Ломоносовские чтения 2021, секция "Физика", 1, (2021).
- Syromyatnikov, A. G., Kudryashov, S. A., Saletsky, A. M., Klavsyuk, A. L. Atomic-scale self-organization of monatomic transition- metal oxide chains. IV International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2021 (IBCM-2021) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 85 (2021).
- Klavsyuk, A. L., Saletsky, A. M., Syromyatnikov, A. G. Magnetism and structure of oxide chains of binary alloys of Co and Ni on Ir(100). IV International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2021 (IBCM-2021) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 138 (2021).
- Dokukin, S. A., Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M. Dendritic growth in Co/Cu(111) surface alloy. IV International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2021 (IBCM-2021) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 114 (2021).
- Kolesnikov, S. V. An improved kinetic Monte Carlo model for computational and analytical investigations of the magnetic properties of finite-size atomic chains. IV International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2021 (IBCM-2021) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 142 (2021).
- Sapronova, E. S., Kolesnikov, S. V. An estimation of magnetic properties of existing and prospective atomic chains in the framework of the Heisenberg Model. IV International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2021 (IBCM-2021) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 190 (2021).
2020 год
Статьи
-
Non-equilibrium island size distribution in one dimension
In this paper, a novel analytical expression for the size distribution of one-dimensional structures at thermodynamic non-equilibrium is derived. The expression is obtained using one-dimensional lattice gas model. Ostwald ripening and decay of short one-dimensional islands is taken into account. The theoretical results are compared with kinetic Monte Carlo simulations and the experimental size distribution of one-dimensional wires. A correct method of extracting the binding energy from the experimental size distribution in one dimension is proposed.
Syromyatnikov, Alexey G., Guseynova, Mujgen R., Saletsky, Alexander M., Klavsyuk, Andrey L. Non-equilibrium island size distribution in one dimension. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2020, 093202 (2020) -
Molecular dynamics simulation of the formation of Cu–Pt nanocontacts in the mechanically controlled break junction experiments
The formation of the Cu–Pt nanocontacts has been investigated by means of classical molecular dynamics simulations. The simulations of the mechanically controlled break junction experiment have been performed in wide ranges of temperatures (0–300 K) and at relative Pt concentrations (0–20%). The structure of the breaking area has been studied 2 ns before the final breaking of the nanocontacts. The length of the breaking area increases with the increase of the temperature and decreases with the increase of the relative Pt concentration. The structure of the breaking area has been investigated by means of the radial distribution function method. The breaking area usually has one of the following structures: (i) a bulk-like structure{,} (ii) a structure consisting of centered icosahedrons rotated 90°{,} or (iii) an icosahedral structure composed of pentagonal rings. The structure of the breaking area is almost independent of the temperature and the stretching direction due to the strong Cu–Pt interaction.
Dokukin, S. A., Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M. Molecular dynamics simulation of the formation of Cu–Pt nanocontacts in the mechanically controlled break junction experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 16136-16142 (2020) -
One-dimensional island size distribution: From non-equilibrium to equilibrium

We present a critical view of the analysis of experimental one-dimensional island size distribution as a function of time. We study the processes of island growth using large-scale kinetic Monte Carlo simulations with diffusion barriers calculated within the framework of the density functional theory. We have shown that one-dimensional island size distribution depends significantly on the time of the experiment. Our model predicts that during annealing or cooling, the transition from one state of thermodynamical equilibrium to another occurs through a non-equilibrium state. This transition consists of Ostwald ripening and decay of one-dimensional islands. The results of our work demonstrate that considering experimental one-dimensional island size distribution as an equilibrium is a big misconception.
Syromyatnikov, Alexey G., Saletsky, Alexander M., Klavsyuk, Andrey L. One-dimensional island size distribution: From non-equilibrium to equilibrium. Surface Science 693, 121528 (2020) -
Diffusion-mediated processes in Pt/Cu(001) surface alloy

In this paper we present the investigation of the diffusion-mediated processes in a Pt/Cu(001) surface alloy. We use the interatomic semiempirical TB-SMA interatomic potentials and the self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo method to investigate the following processes: order-disorder phase transition in the Pt/Cu(001) surface alloy, dissolution of small Pt clusters, and electromigration of small vacancy clusters in the topmost layer of the Pt/Cu(001) surface alloy. We have fitted the universal parameters of the interatomic TB-SMA potentials for the Pt–Cu system. The potentials reproduce bulk properties of copper and platinum as well as properties of the Pt/Cu(001) and Pt/Cu(111) surface alloys.
Dokukin, S. A., Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M., Klavsyuk, A. L. Diffusion-mediated processes in Pt/Cu(001) surface alloy. Surface Science 692, 121515 (2020) -
Моделирование взаимодействия графена с поверхностью меди с помощью модифицированного потенциала Морзе
Предложен новый потенциал взаимодействия углерод-медь, позволяющий моделировать муаровую структуру графена на поверхности меди. Показано, что получающаяся в результате моделирования муаровая структура качественно согласуется с изображениями, полученными с помощью сканирующего туннельного микроскопа. Толщина муаровой структуры и энергия связи графена с поверхностью в пределах погрешности совпадают с известными на сегодняшний день экспериментальными данными. Предложенный потенциал может быть использован и для моделирования диффузии атомов меди по поверхности графена. Исследована диффузия атома и димера меди в широком интервале температур. Обнаружено, что при моделировании диффузии необходимо учитывать вклад колебательной свободной энергии атомов меди.
Колесников, С. В., Сидоренков, А. В., Салецкий, А. М. Моделирование взаимодействия графена с поверхностью меди с помощью модифицированного потенциала Морзе. Письма в ЖЭТФ 111 (2), 101–106 (2020)-
Simulation of the Interaction of Graphene with a Copper Surface Using a Modified Morse Potential
A new carbon–copper interaction potential is proposed to simulate the moiré structure of graphene on the copper surface. It is shown that the resulting moiré structure is in qualitative agreement with scanning tunneling microscopy images. The thickness of the moiré structure and the binding energy of graphene with the surface agree within the error with the existing experimental data. The proposed potential can also be used to simulate the diffusion of copper atoms over the graphene surface. The diffusion of an atom and a copper dimer in a wide temperature range is studied. It is found that the contribution of the vibrational free energy of copper atoms should be taken into account when simulating diffusion.
S. V. Kolesnikov, A. V. Sidorenkov, A. M. Saletsky. Simulation of the Interaction of Graphene with a Copper Surface Using a Modified Morse Potential. JETP Letters 111 (2), 116–120 (2020)
-
-
Stability and magnetism on the atomic scale: Atom-wide wires on vicinal metal substrate
Density functional theory and kinetic Monte Carlo method are applied in our study to describe formation, stability and magnetic properties of atom-wide wires on vicinal metal substrate. We present temperature ranges of atom-wide wires’ formation for different systems. The lifetimes of nanowires were determined, and their stability was discussed. Our calculations for both ferromagnetic Fe and Co wires decorating Pt(775) step edge show that the easy magnetization is in the plane perpendicular to the wire, while for Cu(775) it is oriented along the wire. The wire properties obtained from our simulations will be useful both for creating a new generation of materials and for explaining the experimental data.
Syromyatnikov, Alexey G., Saletsky, Alexander M., Klavsyuk, Andrey L. Stability and magnetism on the atomic scale: Atom-wide wires on vicinal metal substrate. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 510, 166896 (2020) -
Quantum size effect in conductive properties of silver nanofilms
We present the results of our theoretical study of quantum conductance properties of ultrathin silver nanofilms. As the result of our ab initio calculations the quantum size effect in the dependence of electronic conductivity of silver nanofilms on its thickness was found. We revealed the changes in the electronic structure of silver ultrathin nanofilm leading to a change of its conductance properties, which explains the change in the conductive characteristics of ultrathin films observed before in several experimental works. Also we found the emergence of dielectric nature of silver nanofilm conductivity due to changes in its band structure.
K.M. Tsysar, E.M. Smelova, A.M. Saletsky, V.G. Andreev. Quantum size effect in conductive properties of silver nanofilms. Thin Solid Films 710, 138263 (2020) -
Structural Stability of Physisorbed Air-Oxidized Decanethiols on Au(111)

We have studied the dynamic behavior of decanethiol and air-oxidized decanethiol self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on Au(111) using time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy at room temperature. The air-oxidized decanethiols arrange in a lamellae-like structure leaving the herringbone reconstruction of the Au(111) surface intact, indicating a rather weak interaction between the molecules and the surface. Successive STM images show that the air-oxidized molecules are structurally more stable as compared to the nonoxidized decanethiol molecules. This is further confirmed by performing current–time traces with the feedback loop disabled at different locations and at different molecular phases. Density function theory calculations reveal that the diffusion barrier of the physisorbed oxidized decanethiol molecule on Au(111) is about 100 meV higher than the diffusion barrier of a chemisorbed Au-decanethiol complex on Au(111). A two-dimensional activity map of individual current–time traces performed on the air-oxidized decanethiol phase reveals that all the dynamic events take place within the vacancy lines between the air-oxidized decanethiols. These results reveal that the oxidation of thiols provides a pathway to produce more robust and stable self-assembled monolayers at ambient conditions.
Özlem Kap, Nikolai Kabanov, Martina Tsvetanova, Canan Varlikli, Andrey L. Klavsyuk, Harold J. W. Zandvliet, Kai Sotthewes. Structural Stability of Physisorbed Air-Oxidized Decanethiols on Au(111). The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 124 (22), 11977–11984 (2020) -
Моделирование растяжения медно-платиновых наноконтактов методом молекулярной динамики
Методом молекулярной динамики исследовано формирование наноконтактов, состоящих из атомов меди (Cu) и платины (Pt) при различных температурах (0-300 K), относительных концентрациях атомов платины (0-20%) и направлениях растяжения ([100], [110] и [111]). Область разрыва наноконтакта имеет сложную аморфную структуру, для описания которой предложены три модели. Для определения количественного вклада этих моделей в структуру области разрыва проведен анализ ближнего порядка с помощью функций радиального распределения. Исследована зависимость структуры наноконтакта в области разрыва от температуры.
Докукин, С. А., Колесников, С.В., Салецкий, А. М. Моделирование растяжения медно-платиновых наноконтактов методом молекулярной динамики. ЖЭТФ 158 (11), 858 (2020)-
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Elongation of Copper-Platinum Nanocontacts
The formation of nanocontacts consisting of copper (Cu) and platinum (Pt) atoms at various temperatures (0–300 K), relative concentrations of platinum atoms (0–20%), and elongation directions [100], [110], and [111] is investigated using molecular dynamics method. The nanocontact breaking area has a complex amorphous structure, for the description of which we propose three models. To determine the quantitative contributions from these models to the structure of the breaking area, we analyze the short-range order using the radial distribution function. The temperature dependence of the nanocontact structure in the breaking area is analyzed.
S. A. Dokukin, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Elongation of Copper-Platinum Nanocontacts. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 131 (5), 745–751 (2020)
-
Тезисы
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Клавсюк, А. Л., Салецкий, А. М. Распределения длин одномерных наноструктур, или от равновесия к неравновесию и обратно. Сборник тезисов VIII Всероссийской научной молодежной школы-конференции "Химия, физика, биология: пути интеграции", Стр. 39 (2020).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г. Исследование процессов роста атомных проводов на вицинальных металлических поверхностях кинетическим методом Монте-Карло. Материалы Международного молодежного научного форума "Ломоносов-2020", 1, (2020).
2019 год
Статьи
-
Magnetic properties of the finite-length biatomic chains in the framework of the single domain-wall approximation
A simple analytical method for the investigation of the magnetic properties of the finite-length biatomic chains proposed in the framework of the Heisenberg model with uniaxial magnetic anisotropy. The method allows to estimate the reversal time of magnetization of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic biatomic chains. Three cases have been considered: the spontaneous remagnetization, the remagnetization under the interaction with a scanning tunneling microscope, and the remagnetization under the external magnetic field. The applicability limits of the method have been discussed. Within its limits of applicability the method produces the results which are in a perfect agreement with those obtained with the use of the kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. As the examples, two physical systems have been considered: biatomic Fe chains on Cu2 N/Cu(001) surface and biatomic Co chains on Pt(997) surface. The presented method is incomparably less time-consuming than the commonly used kinetic Monte Carlo simulations, especially in the cases of low temperatures or long chains.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Kolesnikova, I. N. Magnetic properties of the finite-length biatomic chains in the framework of the single domain-wall approximation. Physical Review B 100, 224424 (2019) -
Равновесные и неравновесные состояния одномерных атомных структур
Формирование и эволюция одномерных атомных структур были исследованы кинетическим методом Монте-Карло. Обнаружено, что распределение длин таких структур зависит не только от внешних параметров, но и от времени проведения эксперимента. Выявлено, что переход из одного равновесного состояния в другое при нагреве или охлаждении происходит через неравновесное состояние, которое и наблюдается в большинстве экспериментов.
А. Г. Сыромятников, А. М. Салецкий, А. Л. Клавсюк. Равновесные и неравновесные состояния одномерных атомных структур. Письма в ЖЭТФ 110 (5-6(9)), 331–334 (2019)-
Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium States of One-Dimensional Atomic Structures
The formation and evolution of one-dimensional atomic structures have been studied by the kinetic Monte Carlo method. It has been found that the distribution of the lengths of such structures depends not only on external parameters but also on the duration of the experiment. It has been revealed that a transition from one equilibrium state to another at heating or cooling occurs through a nonequilibrium state, which is observed in most of the experiments.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium States of One-Dimensional Atomic Structures. JETP Letters 110 (5), 348–351 (2019)
-
-
Дуффузия димеров атомов при формировании поверхностного сплава Pt/Cu(111)
Представлен результат исследования процессов, происходящих при формировании поверхностного сплава Pt/Cu(111) с помощью самообучающегося кинетического метода Монте Карло. Предложена модель, учитывающая прыжки димеров при формировании гетерогенного сплава на поверхности (111). Исследована роль диффузии димеров при температуре, близкой к комнатной. Установлено относительное количество прыжков димеров на наиболее значимых стадиях формирования сплава Pt/Cu(111).
Докукин, С. А., Колесников, С. В., Салецкий, А. М. Дуффузия димеров атомов при формировании поверхностного сплава Pt/Cu(111). Вестник московского университета Серия 3 ФИЗИКА. АСТРОНОМИЯ (4), 46–51 (2019) -
Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation of small vacancy clusters electromigration on clean and defective Cu(100) surface
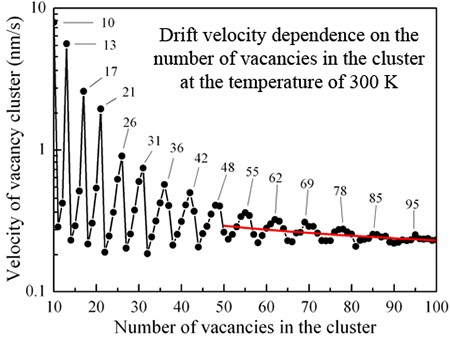
Electromigration of small vacancy clusters on clean and defective Cu(100) surface is investigated on the atomic scale by performing self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. Drift velocity dependencies of vacancy clusters on their size, the substrate temperature, the direction and the absolute value of current density are obtained. The drift velocity dependence on the size of vacancy cluster has an oscillatory behavior. The nature of these oscillations is connected with the difference in diffusion mechanisms of “fast” and “slow” vacancy clusters. The presence of point defects leads to the monotonic decrease of the drift velocity of vacancy clusters. The drift velocity drops down if the diameter of the vacancy cluster is larger than the average distance between the point defects.
Sergey V. Kolesnikov, Alexander M. Saletsky. Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation of small vacancy clusters electromigration on clean and defective Cu(100) surface. The European Physical Journal B 92 (1), 14 (2019) -
Dendritic growth of the Pt-Cu islands on Cu(111) surface: Self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo simulations

Growth of the Pt–Cu islands on the Cu(111) surface at different deposition fluxes, relative amounts of Pt atoms and surface temperatures is investigated on the atomic scale by performing the self-learning kinetic Monte-Carlo simulations. The shape transition of the islands from sixfold symmetry to threefold symmetry with increasing of the relative amount of Pt atoms nPt/nCu in clusters at room temperature was found and explained by the corner diffusion anisotropy. Nonmonotonic dependence of the fractal dimension of the dendritic islands on the ratio nPt/nCu is observed. It is shown that this effect can be interpreted in the framework of the generalized diffusion limited aggregation model if we assume that the dependence of the effective diffusion barrier on the ratio nPt/nCu has the third-degree polynomial function form. This dependence is in qualitative agreement with the analysis of the edge diffusion barriers. The dendritic cluster obtained with the simulations at room temperature looks very similar to the experimentally observed one (Soy et al. (2015)).
S.A. Dokukin, S.V. Kolesnikov, A.M. Saletsky. Dendritic growth of the Pt-Cu islands on Cu(111) surface: Self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. Surface Science 689, 121464 (2019) -
Formation and Stability of Magnetic Atomic Chains on Vicinal Metal Surfaces
A kinetic Monte Carlo method was used to perform large-scale simulation of one-dimensional magnetic nano-structures on vicinal metal surfaces. Temperature ranges for nanochains’ formation were obtained for different systems. The lifetimes of the nanochains were determined, and their stability is discussed. The dependence of chain lifetime on its length is not linear. In order to be usable at room temperature, magnetic Co chains should have a length of 25–30 atoms.
A. Syromyatnikov, A. Klavsyuk, A. Saletsky. Formation and Stability of Magnetic Atomic Chains on Vicinal Metal Surfaces. IEEE Magnetics Letters 10, Art. No. 6111003 (1–3) (2019) -
Magnetization Reversal Time for Ferromagnetic and Antiferromagnetic Chains in the Heisenberg Model
A new analytical method for the study of the magnetic properties of finite-length monatomic and biatomic chains with uniaxial magnetic anisotropy in the framework of the Heisenberg model is described. The method allows the calculation of the reversal time of the magnetization of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic chains. Three cases are considered: spontaneous remagnetization, remagnetization under the interaction with a scanning tunneling microscope, and remagnetization in an external magnetic field. The method gives results that are in good agreement with the results of kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. As examples, two physical systems are considered: biatomic Fe chains on a Cu2 N/Cu(001) surface and biatomic Co chains on a Pt(997) surface.
S. V. Kolesnikov, I. N. Kolesnikova. Magnetization Reversal Time for Ferromagnetic and Antiferromagnetic Chains in the Heisenberg Model. IEEE Magnetics Letters 10, Art. No. 2509105 (1-5) (2019)
Тезисы
- Kolesnikov, S. V. The magnetization reversal time of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic chains in the framework of the Heisenberg Model. The 3rd International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2019 Book of Abstracts, Стр. 51 (2019).
- Klavsyuk, A. L., Syromyatnikov, A. G., Saletsky, A. M. Magnetism and structure on the atomic scale: Atom-wide wires on vicinal metal substrate. The 8th International Workshop on Magnetic Wires (IWMW-2019) Book of Abstracts, Стр. 21 (2019).
- Klavsyuk, A., Syromyatnikov, A., Saletsky, A. Magnetism and structure of atom-wide Co and Fe wires on a metallic substrate. The 3rd International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2019 Book of Abstracts, Стр. 49 (2019).
- Syromyatnikov, A., Klavsyuk, A., Saletsky, A. Formation and structure phase transition of Co nanowires on vicinal Cu(111) surfaces. The 3rd International Baltic Conference on Magnetism 2019 Book of Abstracts, Стр. 159 (2019).
-
Докукин, С. А. Исследование роста дендритов при формировании поверхностного сплава Pt/Cu(111). Конференция Ломоносов 2019, (2019).
-
S. A. Dokukin, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Semiempirical potentials for Pt/Cu(100) surface alloy investigation. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2064 (1), Стр. 030003 (2019).
-
Tsysar, Kseniya M., Andreev, Valery G., Zelensky, V. S., Smelova, E. M., Saletsky, A. M., Vdovin, Vladimir A. Effect of mechanical deformations on absorption spectrum of metallic films of nanometer thickness. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 11022, Стр. 110221J (2019).
2018 год
Статьи
-
Distributions of atomic wire lengths
Controlled growth of metal monatomic wires would enable on-demand tuning of electronic and magnetic properties in this new class of materials. Prior to this work, it was believed that the binding energy can be determined from the distribution of the lengths of the wires. Another misconception was that the antiripening mechanism or quantum effects are responsible for the growth of wires during postdeposition annealing. Combining kinetic Monte Carlo and first-principles density-functional theory calculations, we study the growth of one-dimensional atomic wires on the steps of vicinal surfaces. We show that for a large value of the bond energy, the antiripening mechanism and quantum effects do not affect the length of metal monatomic wires. The conditions under which wires with magic length appear are determined. The observed mechanism of wire growth will be useful both for explaining the experimental data and for creating atomic wires with a given length.
Alexey G. Syromyatnikov, Alexander M. Saletsky, Andrey L. Klavsyuk. Distributions of atomic wire lengths. Physical Review B 97 (23), 235444 (2018) -
Growth of the Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy: self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo simulations

In this paper we present new parameters of the TB-SMA interatomic potentials for the Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy. The parameters are fitted using both the experimental and ab initio data. The potentials reproduce not only the bulk properties of copper and platinum, but also the energy characteristics of the Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy. Growth of the Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy at different Pt concentrations, deposition fluxes, and temperatures is investigated on the atomic scale by performing the self-learning kinetic Monte-Carlo simulations. The main atomic processes responsible for the surface alloy formation and the growth of the finger-like protrusions are identified. The results of our simulations are in a good qualitative agreement with the recent experimental data [J. Chem. Phys. C 118, 3015 (2014)] and can be useful for understanding details of the Pt-Cu interactions at the atomic level.
S.A. Dokukin, S.V. Kolesnikov, A.M. Saletsky, A.L. Klavsyuk. Growth of the Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy: self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 763, 719–727 (2018) -
Bandgap opening in hydrogenated germanene
We have studied the hydrogenation of germanene synthesized on Ge2Pt crystals using scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy. The germanene honeycomb lattice is buckled and consists of two hexagonal sub-lattices that are slightly displaced with respect to each other. The hydrogen atoms adsorb exclusively on the Ge atoms of the upward buckled hexagonal sub-lattice. At a hydrogen exposure of about 100L, the (1×1) buckled honeycomb structure of germanene converts to a (2×2) structure. Scanning tunneling spectra recorded on this (2×2) structure reveal the opening of a bandgap of about 0.2eV. A fully (half) hydrogenated germanene surface is obtained after an exposure of about 9000L hydrogen. The hydrogenated germanene, also referred to as germanane, has a sizeable bandgap of about 0.5eV and is slightly n-type.
Q. Yao, L. Zhang, N. S. Kabanov, A. N. Rudenko, T. Arjmand, H. Rahimpour Soleimani, A. L. Klavsyuk, H. J. W. Zandvliet. Bandgap opening in hydrogenated germanene. Applied Physics Letters 112 (17), 171607 (2018) -
The Au modified Ge(1 1 0) surface
The pristine Ge(1 1 0) surface is composed of Ge pentagons, which are arranged in relatively large (16 × 2) and c(8 × 10) unit cells. The deposition of sub-monolayer amounts of Au and mild annealing results into de-reconstructed Ge(1 1 0) regions completely free of Ge pentagons and regions composed of nanowires that are aligned along the high symmetry [1 -1 0] direction of the Ge(1 1 0) surface. The de-reconstructed Ge(1 1 0) regions consist of atomic rows that are aligned along the [1 -1 0] direction. A substantial fraction of these substrate rows are straight and resemble the atom rows of the unreconstructed, i.e. bulk terminated, Ge(1 1 0) surface, whereas the other substrate rows have a meandering appearance. These meandering atom rows are comprised of two types of atoms, one type that appears dim, whereas the other type appears bright in filled-state scanning tunneling microscopy images. Using density functional theory calculations, we have tested more than 20 different atomic models for the meandering atom rows. The density functional theory calculations reveal that it is energetically favorable for the deposited Au atoms to exchange position with Ge atoms in the first layer. Based on these findings we conclude that the bright atoms are Ge atoms, whereas the dim atoms are Au atoms.
L. Zhang, N.S. Kabanov, P. Bampoulis, A.M. Saletsky, H.J.W. Zandvliet, A.L. Klavsyuk. The Au modified Ge(1 1 0) surface. Applied Surface Science 439, 101–105 (2018) -
Efficient energy basin finding method for atomistic kinetic Monte Carlo models

Presence of energy basins significantly slows down simulations with the kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) method. Various methods of the kMC acceleration are available nowadays, but all of them require efficient energy basin finding algorithm. We present the algorithm providing significant acceleration of the kMC calculations. Use of the acceleration speeds up calculations and allows to reach experimental timescales in simulations. During the simulation of the Pt/Cu(1 1 1) surface alloy formation the acceleration is greater than 5000 times. Results of our simulation qualitatively agree with experiment.
S.A. Dokukin, S.V. Kolesnikov, A.M. Saletsky. Efficient energy basin finding method for atomistic kinetic Monte Carlo models. Computational Materials Science 155, 209–215 (2018) -
Электромиграция малых вакансионных кластеров на поверхности меди (100)
Электромиграция малых вакансионных островов в поверхности Cu(100) исследована с помощью самообучающегося кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Получена зависимость скорости дрейфа вакансионных кластеров от их размера, температуры подложки, величины и направления плотности электрического тока. Показано, что зависимость скорости дрейфа малых кластеров от их размера имеет ярко выраженный осцилляционный характер. Природа этих осцилляций связана с различием в механизмах диффузии "быстрых" и "медленных" кластеров. Установлено, что для корректного моделирования электромиграции вакансионных кластеров необходимо учитывать события, связанные с диффузией димера.
С. В. Колесников, А. М. Салецкий. Электромиграция малых вакансионных кластеров на поверхности меди (100). Письма в ЖЭТФ 101 (1), 19 (2018)-
Electromigration of Small Vacancy Clusters on the (100) Copper Surface
The electromigration of small vacancy islands on the Cu(100) surface has been studied using the self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo method. The dependence of the drift velocity of vacancy clusters on their size, temperature of the substrate, and magnitude and direction of the electric current density has been obtained. It has been shown that the dependence of the drift velocity of small clusters on their size has a pronounced oscillatory character. These oscillations are due to the difference in the mechanisms of diffusion of “fast” and “slow” clusters. It has been found that events associated with the diffusion of dimers should be taken into account for the correct simulation of the electromigration of vacancy clusters.
S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Electromigration of Small Vacancy Clusters on the (100) Copper Surface. JETP Letters 108 (1), 18–22 (2018)
-
-
Зависимость распределения длин атомных цепочек на вицинальной поверхности от внешних параметров
Кинетическим методом Монте-Карло был исследован рост одномерных атомных цепочек вдоль вицинальной поверхности. Показано, что на их рост влияют не значение энергии связи и квантовые эффекты, а исключительно кинетические параметры такие, как температура, поток напыляемых атомов и степень покрытия. Определены условия, при которых появляются цепочки с "магическими длинами".
Сыромятников, А. Г., Салецкий, А. М., Клавсюк, А. Л. Зависимость распределения длин атомных цепочек на вицинальной поверхности от внешних параметров. Письма в ЖЭТФ 107 (12), 794–798 (2018)-
Dependence of the Distribution of Atomic Chain Lengths on a Vicinal Surface on External Parameters
The growth of one-dimensional atomic chains along the vicinal surface has been studied by the kinetic Monte Carlo method. It has been shown that their growth is determined exclusively by kinetic parameters such as the temperature, flux of deposited atoms, and degree of coating rather than by the binding energy and quantum effects. Conditions under which chains with “magic lengths” appear have been determined.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Dependence of the Distribution of Atomic Chain Lengths on a Vicinal Surface on External Parameters. JETP Letters 107 (12), 766–769 (2018)
-
-
Кинетический метод Монте-Карло: математические основы и приложения к физике низкоразмерных наноструктур
Кинетический метод Монте-Карло является незаменимым методом исследования атомных и молекулярных систем, позволяющим решать широкий спектр задач, связанных с диффузией атомов, образованием дефектов и химических соединений различного типа, ростом и самоорганизацией наноструктур. В данной работе рассматриваются основы кинетического метода Монте-Карло и его современные модификации как решеточные, так и нерешеточные. Особое внимание уделено построению самообучающихся алгоритмов на основе различных методов поиска седловых точек потенциальной энергии, а также методам ускорения метода Монте-Карло. Все рассмотренные методы проиллюстрированы актуальными примерами, связанными в основном с физикой поверхности металлов.
С. В. Колесников, А. М. Салецкий, С. А. Докукин, А. Л. Клавсюк. Кинетический метод Монте-Карло: математические основы и приложения к физике низкоразмерных наноструктур. Математическое моделирование 30 (2), 48–80 (2018)-
Kinetic Monte Carlo Method: Mathematical Foundations and Applications for Physics of Low-Dimensional Nanostructures
The kinetic Monte Carlo (kMC) method is an indispensable method for studying atomic and molecular systems, which makes it possible to solve a wide range of problems associated with atomic diffusion, the formation of defects and chemical compounds of various types, as well as the growth and self-organization of nanostructures. In this paper, we consider the fundamentals of the kMC and its modern modifications, both rigid-lattice and off-lattice. Particular attention is focused on constructing self-learning algorithms based on different methods for finding the saddle points of potential energy and on the techniques for the acceleration of the Monte Carlo method. Every considered method is illustrated by relevant examples mostly associated with the physics of metal surfaces.
Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M., Dokukin, S. A., Klavsyuk, A. L. Kinetic Monte Carlo Method: Mathematical Foundations and Applications for Physics of Low-Dimensional Nanostructures. Mathematical Models and Computer Simulations 10 (5), 564-587 (2018)
-
Тезисы
- Dokukin S.A., Kolesnikov S.V., Saletsky A.M., Klavsyuk A.L. Semiempirical potentials for Pt/Cu(100) surface alloy investigation. State-of-the-art Trends of Scientific Research of Artificial and Natural Nanoobjects (STRANN-2018), (2018).
-
Докукин, Сергей Александрович. Моделирование формирования поверхностного сплава Pt/Cu(111) методом самообучающегося кинетического Монте Карло. Материалы Международного молодежного научного форума "ЛОМОНОСОВ-2018", (2018).
- Докукин С.А., Колесников С.В., Салецкий А.М., Клавсюк А.Л. Исследование формирования поверхностного сплава Pt-Cu с помощью метода самообучающегося кинетического Монте Карло. Математика. Компьютер. Образование 2018, (2018).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г., Клавсюк, А. Л., Салецкий, А. М. Моделирование самоорганизации атомных цепочек на ступенчатых поверхностях. {VI} научная молодежная школа-конференция ``Химия, физика, биология: пути интеграции'', Стр. 97–98 (2018).
- Klavsyuk, A. L., Syromyatnikov, A. G., Saletsky, A. M. Co atomic wires on stepped Cu(111) surface: formation, phase transition. International Conference on Nanoscience + Technology (ICN+T) 2018, Стр. 229–230 (2018).
- Kolesnikov S., Dokukin S., Klavsyuk A., Saletsky A. Growth of Pt/Cu(111) surface alloy: fitting of the interatomic potentials and kinetic Monte Carlo simulation. International Conference on Nanoscience + Technology (ICN+T) 2018, (2018).
- Zhang L., Клавсюк А.Л., Кабанов Н.С., Heimbuch R., Салецкий А.М., Zandvliet H.J.W. Structural and electronic properties of Ir/Ge(001) and Au/Ge(110). International Conference on Nanoscience + Technology (ICN+T) 2018, (2018).
- Цысарь К.М., Смелова Е.М., Зеленский В.С., Вдовин В.А., Андреев В.Г. Изменение спектра поглощения нанометровых металлических пленок в ИК и ТГц диапазонах под действием механических дефомаций. 28-я Международная Крымская конференция "СВЧ-техника и телекоммуникационные технологии" (КрыМиКо’2018): материалы конференции, 4, (2018).
- Цысарь К.М., Смелова Е.М., Андреев В.Г., Вдовин В.А. Квантовые размерные эффекты в зависимости электропроводности нанометровых металлических пленок. 28-я Международная Крымская конференция "СВЧ-техника и телекоммуникационные технологии" (КрыМиКо’2018): материалы конференции, (2018).
- Tsysar K.M., Smelova E.M., Zelensky V.S., Andreev V.G., Vdovin V.A. Effect of mechanical deformations on absorption spectrum of metallic films of nanometer thickness. Book of Abstracts of the International Conference “Micro- and Nanoelectronics – 2018” (ICMNE-2018), Стр. 168 (2018).
-
Ekaterina Smelova, Kseniya Tsysar, Alexander Saletsky. Spin-filter state of Au-Co nanowires. EPJ Web of Conferences, 185, Стр. 01019 (2018).
2017 год
Статьи
-
Atomic structure of self-organizing iridium induced nanowires on Ge(001)
The atomic structure of self-organizing iridium (Ir) induced nanowires on Ge(001) is studied by density functional theory (DFT) calculations and variable-temperature scanning tunneling microscopy. The Ir induced nanowires are aligned in a direction perpendicular to the Ge(001) substrate dimer rows, have a width of two atoms and are completely kink-less. Density functional theory calculations show that the Ir atoms prefer to dive into the Ge(001) substrate and push up the neighboring Ge substrate atoms. The nanowires are composed of Ge atoms and not Ir atoms as previously assumed. The regions in the vicinity of the nanowires are very dynamic, even at temperatures as low as 77 K. Time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy measurements reveal that this dynamics is caused by buckled Ge substrate dimers that flip back and forth between their two buckled configurations.
N.S. Kabanov, R. Heimbuch, H.J.W. Zandvliet, A.M. Saletsky, A.L. Klavsyuk. Atomic structure of self-organizing iridium induced nanowires on Ge(001). Applied Surface Science 404, 12–17 (2017) -
Functionalizing Fe adatoms on Cu(001) as a nanoelectromechanical system
This study demonstrates how the spin quantum dynamics of a single Fe atom adsorbed on Cu(001) can be controlled and manipulated by the vibrations of a nearby copper tip attached to a nano cantilever by virtue of the dynamic magnetic anisotropy. The magnetic properties of the composite system are obtained from ab initio calculations in completely relaxed geometries and turned out to be dependent considerably on the tip-iron distance that changes as the vibrations set in. The level populations, the spin dynamics interrelation with the driving frequency, as well as quantum information related quantities are exposed and analyzed.
Michael Schüler, Levan Chotorlishvili, Marius Melz, Alexander Saletsky, Andrey Klavsyuk, Zaza Toklikishvili, Jamal Berakdar. Functionalizing Fe adatoms on Cu(001) as a nanoelectromechanical system. New Journal of Physics 19 (7), 073016 (2017) -
Ab initio investigation of supported Au-Mn nanowires
We present an ab initio study of surface supported Au–Mn nanowires. Three different substrates are discussed: Cu(110), stepped Cu(111) and Si(001) surface. The emergence of stable antiferromagnetic (AFM) solutions in Au–Mn nanowires was found in all three cases. We found the nonzero magnetic moments of Mn atoms, however, the bulk of manganese is paramagnetic. The critical temperature of the Au–Mn wires is calculated by means of kinetic Monte Carlo simulation. The strong size-effect of the critical temperature is demonstrated.
K. M. Tsysar, S. V. Kolesnikov, I. I. Sitnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Ab initio investigation of supported Au-Mn nanowires. Modern Physics Letters B 31 (13), 1750142 (2017) -
Unusual magnetic properties of Au-Mn nanowires on copper and silicon substrates
The quantum properties of bimetallic supported Au–Mn nanowires on copper and silicon substrates were studied. As a result of ab initio calculations it was found that Au–Mn nanowires are antiferromagnetic in the ground state. The strong dependence of magnetic properties of supported Au–Mn nanowires on the substrate geometry and component composition was revealed. Analysis of wire geometry shows that Mn atoms are embedded into the silicon substrate. Results of our study show the strong suppressing of exchange interaction in Au–Mn nanowire on nonmetal silicon substrate in comparison to copper ones. A significant decrease was found for the energy difference ΔE between antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic states of the supported Au–Mn nanowires in comparison to freestanding nanowires as the result of nanowire–substrate interaction.
I. I. Sitnikov, K. M. Tsysar, E. M. Smelova, A. M. Saletsky. Unusual magnetic properties of Au-Mn nanowires on copper and silicon substrates. Physica Status Solidi (B) 254 (7), 1600850 (2017) -
Graphene on Cu(111) at the nonzero temperatures: Molecular dynamic simulation
We present results of molecular dynamic simulation of continuous graphene monolayer on Cu(111). In this paper, we investigate the dependencies of the average binding energy and the average binding distance on the temperature. The interaction between carbon and copper atoms was described by Lennard-Jones potential. It is shown that the binding energy practically remains constant in a wide range of temperatures 0–800 K. However, in the same temperature range, the binding distance of graphene on Cu(111) surface has a linear dependence on temperature. The dependence of the linear thermal expansion coefficient of the binding distance on Lennard-Jones parameters has been calculated. We suggest a simple theoretical model to explain this dependence qualitatively.
A. V. Sidorenkov, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Graphene on Cu(111) at the nonzero temperatures: Molecular dynamic simulation. Modern Physics Letters B 31 (31), 1750289 (2017) -
Формирование и структурный фазовый переход в атомных цепочках Co на поверхности Cu(775)
Кинетическим методом Монте-Карло исследовано формирование атомных цепочек Co на поверхности Сu(775). Выявлено, что длина атомных цепочек Co, формирующихся в результате самоорганизации при эпитаксиальном росте, - величина случайная, а ее среднее значение зависит от параметров эксперимента. В рамках теории функционала плотности обнаружено наличие двух структурных фаз в атомных цепочках. В первой фазе расстояния между атомом и двумя ближайшими соседями в цепочке равны 0.230 нм и 0.280 нм. Во второй фазе атомная цепочка имеет одинаковые межатомные расстояния 0.255 нм. Показано, что температура структурного фазового перехода зависит от длины атомной цепочки.
Сыромятников, А. Г., Кабанов, Н. С., Салецкий, А. М., Клавсюк, А. Л. Формирование и структурный фазовый переход в атомных цепочках Co на поверхности Cu(775). Журнал Экспериментальной и Теоретической Физики 151 (1), 160–164 (2017)-
Formation and structural phase transition in Co atomic chains on a Cu(775) surface
The formation of Co atomic chains on a Cu(775) surface is investigated by the kinetic Monte Carlo method. It is found that the length of Co atomic chains formed as a result of self-organization during epitaxial growth is a random quantity and its mean value depends on the parameters of the experiment. The existence of two structural phases in atomic chains is detected using the density functional theory. In the first phase, the separations between an atom and its two nearest neighbors in a chain are 0.230 and 0.280 nm. In the second phase, an atomic chain has identical atomic spacings of 0.255 nm. It is shown that the temperature of the structural phase transition depends on the length of the atomic chain.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, N. S. Kabanov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Formation and structural phase transition in Co atomic chains on a Cu(775) surface. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 124 (1), 139–142 (2017)
-
-
Оценка времени перемагничивания антиферромагнитных цепочек в рамках модели Гейзенберга
В рамках модели Гейзенберга при наличии одноосной магнитной анизотропии получены формулы, позволяющие оценивать как время спонтанного перемагничивания антиферромагнитной цепочки, так и время перемагничивания при взаимодействии с иглой сканирующего туннельного микроскопа. Вычислены поправки, связанные с возможным отличием свойств крайних атомов цепочки от свойств атомов, находящихся в середине цепочки. Проведены численные оценки для типичных значений параметров гамильтониана Гейзенберга.
Колесников С.В., Колесникова И.Н. Оценка времени перемагничивания антиферромагнитных цепочек в рамках модели Гейзенберга. Журнал Экспериментальной и Теоретической Физики 152 (4), 759–766 (2017)-
An estimate for the magnetization reversal time of antiferromagnetic chains within the Heisenberg model
Within the Heisenberg model in the presence of uniaxial magnetic anisotropy, formulas are obtained that allow one to estimate both the spontaneous magnetization reversal time of an antiferromagnetic chain and the magnetization reversal time due to interaction with the conducting tip of a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). Corrections due to a possible difference between the properties of the end and inner atoms of the chain are calculated. Numerical estimates are obtained for typical parameter values of the Heisenberg Hamiltonian.
S. V. Kolesnikov, I. N. Kolesnikova. An estimate for the magnetization reversal time of antiferromagnetic chains within the Heisenberg model. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 125 (4), 644–650 (2017)
-
-
Размерный эффект в зависимости упругих характеристик тонких медных пленок от толщины
Методами классической молекулярной динамики исследованы продольные упругие деформации свободных медныхпленок и тонких медных пленок, сформированных на поверхности подложки. Обнаружена зависимость упругих свойств медных пленок от толщины и способа формирования пленки. Определены критические значения продольных напряжений и предельные значения упругих деформаций, при которых в пленке возникают необратимые нарушения атомной структуры. Для свободных пленок и пленок на подложках определен момент перехода из области упругости в область пластичности в зависимости от толщины. Рассчитаны критические напряжения, при которых происходит разрушение поверхностного слоя пленки. Полученные данные могут быть использованы для дальнейшего исследования свойств поверхностных наноразмерных структур, изучения влияния деформаций ультратонких металлических пленок на их поглощающие и проводящие свойства, а также на свойства сформированных на их поверхности наноразмерных схем и устройств.
К. М. Цысарь, В. С. Зеленский, В. А. Вдовин, В. Г. Андреев. Размерный эффект в зависимости упругих характеристик тонких медных пленок от толщины. Журнал Радиоэлектроники 12, – (2017)
Тезисы
- Kabanov N.S., Heimbuch R., Zandvliet H.J.W, Saletsky A.M., Klavsyuk A.L. Atomic structure of self-organising iridium induced nanowires on Ge(001). Physics at the borderline between 1D and 2D, Стр. 45 (2017).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г. Формирование атомных цепочек кобальта на поверхности Cu(775). {XXIV} Международная научная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых "Ломоносов-2017", (2017).
-
Кабанов Н.С. Формирование и электронные свойства нанопроводов Au на поверхности Ge(110). {XXIV} Международная научная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых "Ломоносов-2017", (2017).
- Sitnikov I.I., Tsysar K.M., Smelova E.M., Saletsky A.M. Magnetic Au-Mn nanowires on copper and silicon substrates. Moscow international symposium of magnetism "MISM-2017", (2017).
2016 год
Статьи
-
Co diffusion in the near-surface region of Cu
We present our experimental and theoretical study on Co diffusion in the first few atomic layers of Cu(001). While the diffusion of Co atoms in Cu(001) is usually expected to be intense at a temperature T≥800 K, in the vicinity of the surface, it is already activated at a considerably lower temperature T∼650 K whereas the diffusion in the deep bulk region is still inhibited. This intense near-surface diffusion provides an accumulation of Co atoms in the first six atomic layers upon a single stage Co deposition. The details of the near-surface diffusion are studied by analyzing the distribution of the location depth of the buried single Co atoms. The depth of location of single Co atoms is deduced from scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) data. The subsurface Co atoms induce a perturbation of the electron density of states of the surface which is observable as apparent ringlike ripples in the STM images of the atomically flat Cu surface. The depth of location of the buried Co atoms is determined from the diameter of those rings. The largest amount of Co atoms is found to be in the third layer, emphasizing that the near-surface diffusion should be described by diffusion parameters different from those for bulk diffusion. A model that describes the embedding process of Co atoms into Cu(001) layers is developed. The model assumes Co atoms to diffuse via the vacancy and ring-exchange mechanisms. The energy barriers for the interlayer Co diffusion via those mechanisms are calculated using the nudged elastic band method. The model satisfactorily explains the experimental results. Our study reveals that the energy barriers for Co diffusion in the first five atomic layers of Cu(001) are lower than those in the bulk. This defines the region in which Co diffusion should be considered as a near-surface one.
Siahaan, T., Kurnosikov, O., Swagten, H. J. M., Koopmans, B., Kolesnikov, S. V., Saletsky, A. M., Klavsyuk, A. L. Co diffusion in the near-surface region of Cu. Physical Review B 94, 195435 (2016) -
Molecular dynamics simulation of graphene on Cu(111) with different Lennard-Jones parameters
The interaction between graphene and copper (111) surface have been investigated using the molecular dynamics simulations. The range of Lennard-Jones parameters which correspond to the binding energies and the binding distances calculated via ab initio methods was found. The dependencies of the binding energy, the binding distance and the graphene thickness on the parameters of the potential and the rotational angle are presented. We have found minima of the binding energy which can be related to experimentally observed Moiré superstructures.
Alexander V. Sidorenkov, Sergey V. Kolesnikov, Alexander M. Saletsky. Molecular dynamics simulation of graphene on Cu(111) with different Lennard-Jones parameters. The European Physical Journal B 89 (10), 220 (2016) -
The structure phase transition in atom-wide Co wires on a vicinal Cu<111> surface
The ab initio calculations are performed to study the structure of atom-wide Co wire on a vicinal Cu{111} surface. We have found two ferromagnetic states of Co wires. In the first state the Co wire consists of dimers, while in the second state the distance between atoms in Co wire is equal. Using Monte Carlo simulations we demonstrated the structure phase transition in a Co wire. Moreover, the phase transition temperature was determined and the size-effect was studied.
A.G. Syromyatnikov, S.V. Kolesnikov, A.M. Saletsky, A.L. Klavsyuk. The structure phase transition in atom-wide Co wires on a vicinal Cu<111> surface. Materials Letters 179, 69–72 (2016) -
Ab initio study of interaction between 3d adatoms on~the~vicinal~Cu(111) surface
Density functional theory is used to resolve the adatom-step and adatom–adatom interactions on vicinal Cu(111) surface. We demonstrated that the interactions between 3d adatoms appreciably depend on the distance from a surface step. Our calculations show that the magnitude of the repulsive barrier related to the surface step is larger for 3d adatoms located at the upper surface terrace than for adatoms located at the lower surface terrace.
A. G. Syromyatnikov, N. S. Kabanov, A. M. Saletsky, A. L. Klavsyuk. Ab initio study of interaction between 3d adatoms on~the~vicinal~Cu(111) surface. Modern Physics Letters B 30 (17), 1650218 (2016) -
Исследование магнитных свойств атомных цепочек конечной длины при низких температурах
Предложен простой метод, позволяющий в рамках модели Гейзенберга при наличии одноосной магнитной анизотропии вычислять время спонтанного перемагничивания и кривые намагничивания атомных ферромагнитных цепочек конечной длины при низкой температуре. Исследованы пределы применимости метода. Показано, что предложенный метод дает результаты хорошо согласующиеся с результатами моделирования с помощью кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Полученные в рамках нашей модели формулы могут быть также использованы для определения ограничения на температуру Кюри снизу.
Колесников, С. В. Исследование магнитных свойств атомных цепочек конечной длины при низких температурах. Письма в ЖЭТФ 103 (9), 668–672 (2016)-
Low-temperature study of the magnetic properties of finite atomic chains
A simple method for the calculation of the spontaneous remagnetization time and magnetization curves of atomic finite-length ferromagnetic chains at a low temperature within the Heisenberg model has been proposed. The applicability limits of the method have been studied. It has been shown that the proposed method gives results being in good agreement with the kinetic Monte Carlo simulation results. Formulas obtained within our model can also be used to determine the lower bound for the Curie temperature.
S. V. Kolesnikov. Low-temperature study of the magnetic properties of finite atomic chains. JETP Letters 103 (9), 588–592 (2016)
-
-
Магнитные характеристики AU–MN нанопроводов
В работе проведено теоретическое исследование из первых принципов квантовых свойств Au-Mn нанопроводов. Обнаружено появление магнитных свойств Au-Mn нанопроводов, состоящих из немагнитных элементов. В работе обнаружено появление магнитных моментов у атомов марганца ~4.3 μB значительной величины, при том, что в кристаллическом состоянии марганец является парамагнетиком. Исследование электронной структуры нанопровода показало, что формирование сложной структуры гибридных орбиталей поддерживает существование магнитных моментов у атомов марганца в биметаллическом нанопроводе. Кроме того, в работе обнаружена стабилизация антиферромагнитного решения в Au-Mn нанопроводах посредством формирования косвенного обменного взаимодействия между атомами марганца в нанопроводе.
И. И. Ситников, К. М. Цысарь, Е. М. Смелова, А. М. Салецкий. Магнитные характеристики AU–MN нанопроводов. Письма в ЖЭТФ 103 (9), 673–678 (2016)-
Magnetic characteristics of Au-Mn nanowires
The quantum properties of Au–Mn nanowires are analyzed theoretically from first principles. The emergence of magnetic properties in these nanowires, consisting of nonmagnetic elements, is demonstrated. It is shown that the manganese atoms carry fairly large magnetic moments (~4.3 μB), although crystalline Mn is a paramagnet. Analysis of the electronic structure of these bimetallic nanowires indicates that the magnetic moments at the Mn atoms arise owing to the formation of a complicated structure of hybrid orbitals. Furthermore, it is found that the antiferromagnetic state in Au–Mn nanowires is stabilized by the occurrence of indirect exchange interaction between Mn atoms.
I. I. Sitnikov, K. M. Tsysar, E. M. Smelova, A. M. Saletsky. Magnetic characteristics of Au-Mn nanowires. JETP Letters 103 (9), 593–597 (2016)
-
Тезисы
- Klavsyuk, A. L., Syromyatnikov, A. G., Kabanov, N. S. Ab initio study of structure transition in atom-wide Co wires on a vicinal Cu(111) surface. European Conference on Surface Science (ECOSS 32), Стр. 443 (2016).
-
Сыромятников, А. Г. Структурный фазовый переход в нанопроводах кобальта. XXIII Международная научная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых "Ломоносов-2016", (2016).
- S. Kolesnikov, A. Sidorenkov, A. Saletsky. Molecular dynamics simulation of graphene on Cu(111) with different Lennard-Jones parameters. European Conference on Surface Science (ECOSS 32), Стр. 128 (2016).
-
Ekaterina M. Smelova, Ivan I. Sitnikov, Vladimir S. Zelensky, Kseniya M. Tsysar, Valery G. Andreev, Vladimir A. Vdovin, Alexander M. Saletsky. Mechanical properties of bimetallic one-dimensional structures. International Conference on Micro- and Nano-Electronics 2016, (2016).
-
Kseniya M. Tsysar, Valery G. Andreev, Vladimir A. Vdovin. Effective optical constants of silver nanofilms calculated in wide frequency range. International Conference on Micro- and Nano-Electronics 2016, (2016).
-
Докукин, Сергей Александрович. Теоретическое исследование формирования поверхностного сплава платина-медь. Материалы Международного молодежного научного форума "ЛОМОНОСОВ-2016", (2016).
2015 год
Статьи
-
SnSi nanocrystals of zinc-blende structure in a Si matrix
A zinc-blende (sphalerite) crystallographic structure of SnSi nanocrystals generated by molecular-beam epitaxy is observed by electron microscopy techniques in a Si matrix. Ab initio density-functional modeling reveals a stabilizing effect of the Si matrix, which results in the lowest formation enthalpy of SnSi nanocrystals having the unexpected zinc-blende structure. Such nanocrystals could be applied in Si photonics to function as non-centrosymmetric media for the nonlinear optical process of second harmonic generation.
Alexander Tonkikh, Andrey Klavsyuk, Nikolay Zakharov, Alexander Saletsky, Peter Werner. SnSi nanocrystals of zinc-blende structure in a Si matrix. Nano Research 8 (12), 3905–3911 (2015) -
Формирование и свойства металлических атомных контактов
Рассматривается одна из актуальных и многообещающих областей современной физики — изучение физических свойств металлических наноконтактов, состоящих из нескольких атомов. Привлекательность атомных контактов обусловлена не только перспективностью их практического применения, но и возможностью проверки с их помощью различных теоретических подходов посредством сравнения теоретических результатов с экспериментальными данными. Особое внимание уделено теоретическим подходам к изучению процессов формирования и исследованиям свойств металлических атомных контактов.
А. Л. Клавсюк, А. М. Салецкий. Формирование и свойства металлических атомных контактов. Успехи физических наук 185 (10), 1009-1030 (2015)-
Formation and properties of metallic atomic contacts
One of most topical and promising areas in present-day physics is the study of the physical properties of metallic few-atom contacts, which are attractive not only for their application prospects, but also because of their amenability to verification through theory-versus-experiment comparison. This review mainly focuses on theoretical approaches to understanding the formation processes and properties of metallic atomic contacts.
A. L. Klavsyuk, A. M. Saletsky. Formation and properties of metallic atomic contacts. Physics-Uspekhi 58 (10), 933-951 (2015)
-
-
Magnetization dynamics of mixed Co-Au chains on Cu(110) substrate: Combinedab initioand kinetic Monte Carlo study
We present an investigation of the one-dimensional ferromagnetism in Au-Co nanowires deposited on the Cu(110) surface. By using the density functional theory, the influence of the nonmagnetic copper substrate Cu(110) on the magnetic properties of the bimetallic Au-Co nanowires is studied. The results show the emergence of magnetic anisotropy in the supported Au-Co nanowires. The magnetic anisotropy energy has the same order of magnitude as the exchange interaction energy between Co atoms in the wire. Our electronic structure calculation reveals the emergence of new hybridized bands between Au and Co atoms and surface Cu atoms. The Curie temperature of the Au-Co wires is calculated by means of kinetic Monte Carlo simulation. The strong size effect of the Curie temperature is demonstrated.
K. M. Tsysar, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Magnetization dynamics of mixed Co-Au chains on Cu(110) substrate: Combinedab initioand kinetic Monte Carlo study. Chinese Physics B 24 (9), 097302 (2015) -
Fe and Co nanostructures embedded into the Cu(100) surface: Self-Organization and magnetic properties
The self-organization and magnetic properties of small iron and cobalt nanostructures embedded into the first layer of a Cu(100) surface are investigated using the self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo method and density functional theory. The similarities and differences between the Fe/Cu(100) and the Co/Cu(100) are underlined. The time evolution of magnetic properties of a copper monolayer with embedded magnetic atoms at 380 K is discussed.
S. V. Kolesnikov, A. L. Klavsyuk, A. M. Saletsky. Fe and Co nanostructures embedded into the Cu(100) surface: Self-Organization and magnetic properties. Журнал экспериментальной и теоретической физики 148 (4), 706–713 (2015)-
Fe and Co nanostructures embedded into the Cu(100) surface: Self-Organization and magnetic properties
The self-organization and magnetic properties of small iron and cobalt nanostructures embedded into the first layer of a Cu(100) surface are investigated using the self-learning kinetic Monte Carlo method and density functional theory. The similarities and differences between the Fe/Cu(100) and the Co/Cu(100) are underlined. The time evolution of magnetic properties of a copper monolayer with embedded magnetic atoms at 380 K is discussed.
S. V. Kolesnikov, A. L. Klavsyuk, A. M. Saletsky. Fe and Co nanostructures embedded into the Cu(100) surface: Self-Organization and magnetic properties. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics 121 (4), 616–622 (2015)
-
-
Магнитные свойства одномерных цепочек Au-Co на поверхности меди(110)
В рамках теории функционала электронной плотности вычислены магнитные свойства атомов кобальта в цепочках Au-Co на поверхности Cu(110), такие как магнитный момент, энергия магнитной анизотропии, обменный интеграл. Обнаружено, при нулевой температуре бесконечно длинная цепочка Au-Co находится в ферромагнитном состоянии. Магнитостатические и магнитодинамические свойства цепочек Au-Co конечной длины при отличной от нуля температуре исследованы в рамках модели Гейзенберга с помощью кинетического метода Монте-Карло. Получены зависимости температуры Кюри и времени спонтанного перемагничивания от длины цепочки, а также зависимости коэрцитивной силы цепочки от температуры, длины цепочки и скорости перемагничивания. При выполнении работы использованы вычислительные ресурсы Научно-исследовательского вычислительного центра Московского государственного университета им. М.В. Ломоносова (НИВЦ МГУ).
Колесников С.В., Цысарь К.М., Салецкий А.М. Магнитные свойства одномерных цепочек Au-Co на поверхности меди(110). Физика твердого тела 57 (8), 1492–1497 (2015)-
Magnetic properties of one-dimensional Au-Co chains on the copper(110) surface
Magnetic properties of cobalt atoms in Au-Co chains on the Cu(110) surface (such as the magnetic moment, magnetic anisotropy energy, and exchange energy) have been calculated in the framework of the density functional theory. It has been found, at zero temperature, an infinitely long Au-Co chain is in the ferromagnetic state. The magnetostatic and magnetodynamic properties of finite-length Au-Co chains at a nonzero temperature have been investigated within the Heisenberg model using the kinetic Monte Carlo method. The dependences of the Curie temperature and magnetization reversal time on the chain length have been obtained, as well as the dependences of the coercivity of the chain on the temperature, chain length, and magnetization reversal rate.
S. V. Kolesnikov, K. M. Tsysar, A. M. Saletsky. Magnetic properties of one-dimensional Au-Co chains on the copper(110) surface. Physics of the Solid State 57 (8), 1513–1518 (2015)
-
Тезисы
- Andrey Klavsyuk, Denis Nagayuk, Alexander Saletsky, Alexander Tonkikh, Nikolai Zakharov, Peter Werner. Stability and Electronic band structure of SnSi Nanocrystals in a Si Matrix. Book of Abstracts, European Conference on Surface Science (ECOSS 31), Стр. 553 (2015).
- Nikolay Kabanov, Alexander Saletsky, Andrey Klavsyuk. Atomic structure of Ir nanowires on Ge(001). Book of Abstracts, European Conference on Surface Science (ECOSS 31), Стр. 554 (2015).
-
Сыромятников А. Г. Определение структуры нанопроводов Co на вицинальной поверхности Cu(111) методом молекулярной динамики. XXII Международная научная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых "Ломоносов-2015", (2015).
-
Кабанов Н.С. Исследование структуры нанопроводов Ir на поверхности Ge(001). XXII Международная научная конференция студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых "Ломоносов-2015", (2015).
2014 год
Статьи
-
Emergence of spin-filter states in Pt-Fe nanowires
Our theoretical study predicts the emergence of a new spin-filter state in one-dimensional Pt–Fe bimetallic nanowires. The results show the existence of two transmission states in contracted “zig-zag” Pt–Fe nanowires with low and high transmission 1G<sub>0</sub> and 3G<sub>0</sub>, correspondingly, and one transmission state in linear stretched nanowires with conductance 2G<sub>0</sub>. Our first principle calculations revealed the dependence of quantum conductance of Pt–Fe nanowires on their geometry and atomic structure. Thus we found that nanowire stretching up to the interatomic distance of 2.3 Å leads to the transition of the wire from a “zig-zag” to the linear configuration, leading to changes in the conductance properties of the wire, i.e. formation of a new spin-filter state. Our study shows also the emergence of a magnetic transition from ferromagnetic to antiferromagnetic states under wire stretching. We found that the spin-filter state exists only in “zig-zag” Pt–Fe nanowires in the ferromagnetic state. Moreover, the spin-polarization of quantum electron transport through Pt–Fe nanowires vanishes totally in linear stretched nanowires in an antiferromagnetic state. Our electronic structure calculation reveals the emergence of new hybridized states in the band structure of the Pt–Fe nanowire, which causes the formation of a new spin-filter state.
E. M. Smelova, K. M. Tsysar, A. M. Saletsky. Emergence of spin-filter states in Pt-Fe nanowires. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16 (18), 8360–8366 (2014) -
Effect of alloying of magnetic and non-magnetic low reactivity atoms into atomic chain
We have theoretically studied the possible formation of evenly mixed Pt–X, Au–X, Pd–X bimetallic atomic chains (ACs) with X = Co, Fe, and Ni. The results show that Pt–Fe ACs are the most energetically favorable. First principles calculations revealed that the energy of alloy formation is dependent on the d‐band filling of the magnetic component (Fe, Co, and Ni). Thus, we found that formation of stable evenly mixed ACs with Ni atoms as the magnetic component is not possible. Moreover, we found that the alloying energy is dependent on the geometry of the AC. We found that the energy of alloy formation remains unchanged in linear ACs and drastically decreases by ∼1 eV under chain contraction, accompanied by a transition of the AC from a linear to a zigzag configuration. Our electronic structure calculations revealed the emergence of a ferromagnetic transition under stretching of the AC in all the bimetallic chains with Fe atoms as the magnetic component (Pt–Fe, Pd–Fe, and Au–Fe) from the ferromagnetic to the antiferromagnetic state.
Kseniya M. Tsysar, Dmitry I. Bazhanov, Ekaterina M. Smelova, Alexander M. Saletsky. Effect of alloying of magnetic and non-magnetic low reactivity atoms into atomic chain. Physica Status Solidi (B) 251 (4), 871–876 (2014) -
Самоорганизация наноструктур из атомов железа в первом слое поверхности меди (100)
Методом молекулярной динамики и кинетическим методом Монте-Карло исследованы механизмы диффузии поверхностных вакансий и атомов железа в первом слое поверхности Cu(100). Диффузия погруженных атомов приводит к самоорганизации связанных наноструктур из атомов железа. Получены зависимости количества наиболее распространенных наноструктур от времени. Согласно полученным результатам самоорганизацию погруженных наноструктур можно разделить на три этапа, на которых поверхность меди обладает существенно различной морфологией.
С. В. Колесников. Самоорганизация наноструктур из атомов железа в первом слое поверхности меди (100). Письма в ЖЭТФ 99 (5), 329–332 (2014)-
Self-organization of iron-atom nanostructures in the first layer of the (100) copper surface
Mechanisms of the diffusion of surface vacancies and iron atoms in the first layer of the Cu(100) surface have been studied by molecular dynamics and the kinetic Monte Carlo method. The diffusion of embedded atoms results in the self-organization of bound iron-atom nanostructures. The time dependences of the number of most widespread nanostructures have been obtained. According to the results, the self-organization of embedded nanostructures can be divided into three stages in which the copper surface has significantly different morphologies.
S. V. Kolesnikov. Self-organization of iron-atom nanostructures in the first layer of the (100) copper surface. JETP Letters 99 (5), 286–289 (2014)
-
-
Исследование взаимодействия адатомов Co на вицинальной поверхности Сu(111)
В рамках теории функционала электронной плотности методом гриновских функций Корринги-Кона-Ростокера вычислены энергии взаимодействия адатомов Co на вицинальной поверхности Сu(111). Продемонстрировано, что взаимодействие между адатомами Co существенным образом зависит от расстояния до ступени. Наши расчеты показали, что значение отталкивающего барьера ступени для адатома Co на верхней террасе больше, чем на нижней.
А. Г. Сыромятников, А. Л. Клавсюк, А. М. Салецкий. Исследование взаимодействия адатомов Co на вицинальной поверхности Сu(111). Письма в ЖЭТФ 100 (1), 26–29 (2014)-
Analysis of Interactions between Co Adatoms on the Vicinal Cu(111) Surface
The energies of magnetic interactions between Co adatoms at the vicinal Cu(111) surface are calculated in the framework of the density functional theory using the Korringa-Kohn-Rostoker type Green’s functions. It is demonstrated that the interactions between Co adatoms appreciably depend on the distance from a surface step. Our calculations show that the magnitude of the repulsive barrier related to the surface step is larger for Co adatoms located at the upper surface terrace than for those located at the lower surface terrace.
Syromyatnikov, A. G., Klavsyuk, A. L., Saletsky, A. M. Analysis of Interactions between Co Adatoms on the Vicinal Cu(111) Surface. JETP Letters 100 (1), 24–27 (2014)
-
-
Магнитные свойства нанокластеров Fe и Co, погруженных в первый слой поверхности Cu(100)
В рамках теории функционала электронной плотности вычислены энергии магнитной анизотропии, а также спиновые и орбитальные магнитные моменты атомов, входящих в простейшие наноструктуры, формирующиеся в результате самоорганизации в первом слое поверхности Cu(100). Показана критическая роль релаксации поверхности при вычислении энергии магнитной анизотропии, приводящая для нанокластеров из атомов железа к повороту оси легкого намагничивания.
Клавсюк, А. Л., Колесников, С. В., Салецкий, А. М. Магнитные свойства нанокластеров Fe и Co, погруженных в первый слой поверхности Cu(100). Письма в ЖЭТФ 99 (1), 750–753 (2014)-
Magnetic properties of Fe and Co nanoclusters embedded in the first Cu(100) surface layer
The magnetic anisotropy energies, as well as spin and orbital magnetic moments of the atoms involved in the simplest nanostructures formed due to the self-organization within the first Cu(100) surface layer, are calculated in the framework of the density functional theory. The critical role of the surface relaxation, which leads to the rotation of the easy magnetization axis in iron nanoclusters, is demonstrated in the calculations of magnetic anisotropy.
A. L. Klavsyuk, S. V. Kolesnikov, A. M. Saletsky. Magnetic properties of Fe and Co nanoclusters embedded in the first Cu(100) surface layer. JETP Letters 99 (11), 646–649 (2014)
-
-
Электронная квантовая проводимость биметаллических Pt–Fe нанопроводов
Смелова, Е. М., Цысарь, К. М., Салецкий, А. М. Электронная квантовая проводимость биметаллических Pt–Fe нанопроводов. Известия Российской академии наук. Серия физическая 78 (2), 220–222 (2014)